Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Alipov et al. Difference between native and desialylated LDL
apoA-IV, and apoF], associated with inflammation
(apoD, apoJ, apoM, serum amyloid A4, paraoxonase 1,
prenylcysteine oxidase 1, migration inhibitory factor-
related protein 8, and retinol binding protein), related with
thrombosis (fibrinogen alpha chain) and components
of the innate immunity system (lysozyme C, alpha-1
antitripsin, apoL-1, and transthyretin). [10] ApoB-100 is a
large glycoprotein, which stabilizes and maintains LDL
structure and composition. ApoB-100 has 24 potential
N-glycosylation sites, with up to 16 asparagine residues
actually glycosylated. Carbohydrates, including neutral
and acidic carbohydrate chains, account for 5-9%
of apoB-100 molecular weight. All chains contain
N-acetylglucosamine and mannose residues. Acidic
chains contain terminal sialic acid residues followed
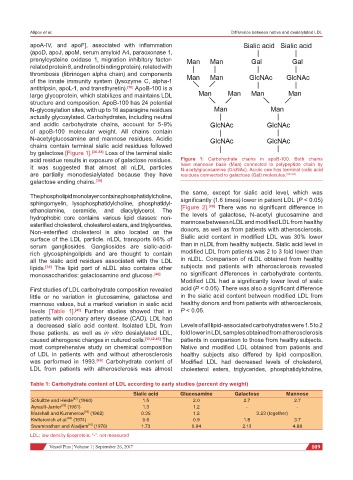
by galactose [Figure 1]. [36-38] Loss of the terminal sialic
acid residue results in exposure of galactose residues. Figure 1: Carbohydrate chains in apoB-100. Both chains
It was suggested that almost all nLDL particles have mannose base (Man) connected to polypeptide chain by
N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Acidic one has terminal sialic acid
are partially monodesialylated because they have residues connected to galactose (Gal) molecules. [36-38]
galactose ending chains. [39]
the same, except for sialic acid level, which was
The phospholipid monolayer contains phosphatidylcholine, significantly (1.6 times) lower in patient LDL (P < 0.05)
sphingomyelin, lysophosphatidylcholine, phosphatidyl- [Figure 2]. [40] There was no significant difference in
ethanolamine, ceramide, and diacylglycerol. The
hydrophobic core contains various lipid classes: non- the levels of galactose, N-acetyl glucosamine and
esterified cholesterol, cholesterol esters, and triglycerides. mannose between nLDL and modified LDL from healthy
Non-esterified cholesterol is also located on the donors, as well as from patients with atherosclerosis.
surface of the LDL particle. nLDL transports 66% of Sialic acid content in modified LDL was 30% lower
serum gangliosides. Gangliosides are sialic-acid- than in nLDL from healthy subjects. Sialic acid level in
rich glycosphingolipids and are thought to contain modified LDL from patients was 2 to 3 fold lower than
all the sialic acid residues associated with the LDL in nLDL. Comparison of nLDL obtained from healthy
lipids. [36] The lipid part of nLDL also contains other subjects and patients with atherosclerosis revealed
monosaccharides: galactosamine and glucose. [40] no significant differences in carbohydrate contents.
Modified LDL had a significantly lower level of sialic
First studies of LDL carbohydrate composition revealed acid (P < 0.05). There was also a significant difference
little or no variation in glucosamine, galactose and in the sialic acid content between modified LDL from
mannose values, but a marked variation in sialic acid healthy donors and from patients with atherosclerosis,
levels [Table 1]. Further studies showed that in P < 0.05.
[41]
patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), LDL had
a decreased sialic acid content. Isolated LDL from Levels of all lipid-associated carbohydrates were 1.5 to 2
these patients, as well as in vitro desialylated LDL, fold lower in LDL samples obtained from atherosclerosis
caused atherogenic changes in cultured cells. [13,42,43] The patients in comparison to those from healthy subjects.
most comprehensive study on chemical composition Native and modified LDL obtained from patients and
of LDL in patients with and without atherosclerosis healthy subjects also differed by lipid composition.
was performed in 1993. [40] Carbohydrate content of Modified LDL had decreased levels of cholesterol,
LDL from patients with atherosclerosis was almost cholesterol esters, triglycerides, phosphatidylcholine,
Table 1: Carbohydrate content of LDL according to early studies (percent dry weight)
Sialic acid Glucosamine Galactose Mannose
Schultze and Heide [87] (1960) 1.5 2.0 2.7 2.7
Ayrault-Jarrier [88] (1961) 1.3 1.2 - -
Marshall and Kummerow [89] (1962) 0.35 1.2 3.23 (together)
Kwiterovich et al. [90] (1974) 0.6 0.9 1.8 3.7
[41]
Swaminathan and Aladjem (1976) 1.73 0.94 2.13 4.88
LDL: low density lipoprotein; “-”: not measured
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017 109