Page 167 - Read Online
P. 167
Page 10 of 28 Wang et al. Soft Sci. 2026, 6, 8
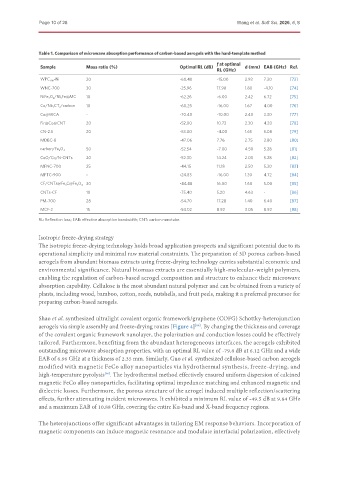
Table 1. Comparison of microwave absorption performance of carbon-based aerogels with the hard-template method
f at optimal
Sample Mass ratio (%) Optimal RL (dB) d (mm) EAB (GHz) Ref.
RL (GHz)
WPC 700 -Ni 20 -60.40 ~15.00 2.93 7.30 [73]
WNC-700 30 -25.96 17.98 1.80 -4.10 [74]
NiFe 2 O 4 /Ni 3 Fe@MC 10 -62.26 ~6.00 2.42 6.72 [75]
Co/Nb 2 CT x /carbon 10 -60.25 ~16.00 1.67 4.00 [76]
Co@WCA - -70.40 ~10.00 2.40 3.30 [77]
Fir@Co@CNT 20 -52.00 10.72 2.30 4.20 [78]
CN-2.5 20 -53.00 ~4.00 1.65 5.08 [79]
MDBC-8 -47.06 7.76 2.75 2.80 [80]
50 -52.54 ~7.00 4.50 5.28 [81]
carbon/Fe 3 O 4
CoO/Co/N-CNTs 20 -52.30 14.24 2.00 5.28 [82]
MFNC-700 25 -44.15 11.18 2.50 5.30 [83]
MFTC-900 - -24.83 ~16.00 1.30 4.72 [84]
CF/CNTs@Fe 3 C@Fe 3 O 4 30 -44.48 16.00 1.68 5.00 [85]
CNTs-CF 10 -75.40 5.20 4.63 - [86]
PM-700 28 -54.70 17.28 1.40 6.40 [87]
MCF-2 15 -54.02 8.92 3.05 8.92 [88]
RL: Reflection loss; EAB: effective absorption bandwidth; CNT: carbon nanotube.
Isotropic freeze-drying strategy
The isotropic freeze-drying technology holds broad application prospects and significant potential due to its
operational simplicity and minimal raw material constraints. The preparation of 3D porous carbon-based
aerogels from abundant biomass extracts using freeze-drying technology carries substantial economic and
environmental significance. Natural biomass extracts are essentially high-molecular-weight polymers,
enabling the regulation of carbon-based aerogel composition and structure to enhance their microwave
absorption capability. Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer and can be obtained from a variety of
plants, including wood, bamboo, cotton, reeds, nutshells, and fruit peels, making it a preferred precursor for
preparing carbon-based aerogels.
Shao et al. synthesized ultralight covalent organic framework/graphene (COFG) Schottky-heterojunction
aerogels via simple assembly and freeze-drying routes [Figure 4] . By changing the thickness and coverage
[89]
of the covalent organic framework nanolayer, the polarization and conduction losses could be effectively
tailored. Furthermore, benefiting from the abundant heterogeneous interfaces, the aerogels exhibited
outstanding microwave absorption properties, with an optimal RL value of -79.8 dB at 6.12 GHz and a wide
EAB of 6.96 GHz at a thickness of 2.35 mm. Similarly, Guo et al. synthesized cellulose-based carbon aerogels
modified with magnetic FeCo alloy nanoparticles via hydrothermal synthesis, freeze-drying, and
high-temperature pyrolysis . The hydrothermal method effectively ensured uniform dispersion of calcined
[90]
magnetic FeCo alloy nanoparticles, facilitating optimal impedance matching and enhanced magnetic and
dielectric losses. Furthermore, the porous structure of the aerogel induced multiple reflection/scattering
effects, further attenuating incident microwaves. It exhibited a minimum RL value of -49.5 dB at 9.84 GHz
and a maximum EAB of 10.88 GHz, covering the entire Ku-band and X-band frequency regions.
The heterojunctions offer significant advantages in tailoring EM response behaviors. Incorporation of
magnetic components can induce magnetic resonance and modulate interfacial polarization, effectively