Page 168 - Read Online
P. 168
Wang et al. Soft Sci. 2026, 6, 8 Page 11 of 28
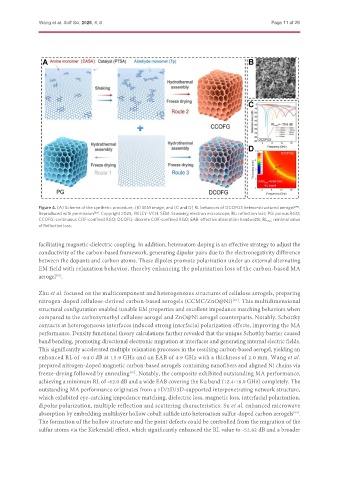
Figure 4. (A) Scheme of the synthetic procedure, (B) SEM image, and (C and D) RL behaviors of DCOFG3 hetero-structured aerogel [89] .
Reproduced with permission [89] . Copyright 2025, WILEY-VCH. SEM: Scanning electron microscope; RL: reflection loss; PG: porous RGO;
CCOFG: continuous COF-confined RGO; DCOFG: discrete COF-confined RGO; EAB: effective absorption bandwidth; RL min : minimal value
of Reflection loss.
facilitating magnetic-dielectric coupling. In addition, heteroatom doping is an effective strategy to adjust the
conductivity of the carbon-based framework, generating dipolar pairs due to the electronegativity difference
between the dopants and carbon atoms. These dipoles promote polarization under an external alternating
EM field with relaxation behavior, thereby enhancing the polarization loss of the carbon-based MA
aerogel .
[91]
Zhu et al. focused on the multicomponent and heterogeneous structures of cellulose aerogels, preparing
nitrogen-doped cellulose-derived carbon-based aerogels (CCMC/ZnO@Ni) . This multidimensional
[92]
structural configuration enabled tunable EM properties and excellent impedance matching behaviors when
compared to the carboxymethyl cellulose aerogel and ZnO@Ni aerogel counterparts. Notably, Schottky
contacts at heterogeneous interfaces induced strong interfacial polarization effects, improving the MA
performance. Density functional theory calculations further revealed that the unique Schottky barrier caused
band bending, promoting directional electronic migration at interfaces and generating internal electric fields.
This significantly accelerated multiple relaxation processes in the resulting carbon-based aerogel, yielding an
enhanced RL of -64.0 dB at 13.9 GHz and an EAB of 4.9 GHz with a thickness of 2.0 mm. Wang et al.
prepared nitrogen-doped magnetic carbon-based aerogels containing nanofibers and aligned Ni chains via
freeze-drying followed by annealing . Notably, the composite exhibited outstanding MA performance,
[93]
achieving a minimum RL of -62.0 dB and a wide EAB covering the Ku band (12.4-18.0 GHz) completely. The
outstanding MA performance originates from a 1D/2D/3D-supported interpenetrating network structure,
which exhibited eye-catching impedance matching, dielectric loss, magnetic loss, interfacial polarization,
dipolar polarization, multiple reflection and scattering characteristics. Su et al. enhanced microwave
absorption by embedding multilayer hollow cobalt sulfide into heteroatom sulfur-doped carbon aerogels .
[94]
The formation of the hollow structure and the point defects could be controlled from the migration of the
sulfur atoms via the Kirkendall effect, which significantly enhanced the RL value to -52.82 dB and a broader