Page 143 - Read Online
P. 143
Research Article | Open Access
Soft Science
Ding et al. Soft Sci. 2026, 6, 2 DOI:10.20517/ss.2025.113
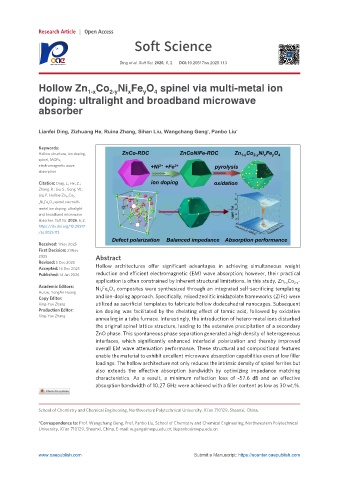
Hollow Zn Co Ni Fe O spinel via multi-metal ion
y
4
2-y
1-x
x
doping: ultralight and broadband microwave
absorber
Lianfei Ding, Zizhuang He, Ruina Zhang, Sihan Liu, Wangchang Geng , Panbo Liu *
*
Keywords:
Hollow structure, ion doping,
spinel, MOFs,
electromagnetic wave
absorption
Citation: Ding, L.; He, Z.;
Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Geng, W.;
Liu, P. Hollow Zn 1-x Co 2-
y Ni x Fe y O 4 spinel via multi-
metal ion doping: ultralight
and broadband microwave
absorber. Soft Sci. 2026, 6, 2.
https://dx.doi.org/10.20517
/ss.2025.113
Received: 1 Nov 2025
First Decision: 21 Nov
2025 Abstract
Revised: 5 Dec 2025
Accepted: 16 Dec 2025 Hollow architectures offer significant advantages in achieving simultaneous weight
Published: 14 Jan 2026 reduction and efficient electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption; however, their practical
application is often constrained by inherent structural limitations. In this study, Zn 1‑x Co 2‑y -
Academic Editors: Ni x Fe y O 4 composites were synthesized through an integrated self-sacrificing templating
Hu Liu, YongAn Huang
Copy Editor: and ion-doping approach. Specifically, mixed zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) were
Xing-Yue Zhang utilized as sacrificial templates to fabricate hollow dodecahedral nanocages. Subsequent
Production Editor: ion doping was facilitated by the chelating effect of tannic acid, followed by oxidative
Xing-Yue Zhang
annealing in a tube furnace. Interestingly, the introduction of hetero-metal ions disturbed
the original spinel lattice structure, leading to the extensive precipitation of a secondary
ZnO phase. This spontaneous phase separation generated a high density of heterogeneous
interfaces, which significantly enhanced interfacial polarization and thereby improved
overall EM wave attenuation performance. These structural and compositional features
enable the material to exhibit excellent microwave absorption capabilities even at low filler
loadings. The hollow architecture not only reduces the intrinsic density of spinel ferrites but
also extends the effective absorption bandwidth by optimizing impedance matching
characteristics. As a result, a minimum reflection loss of -57.6 dB and an effective
absorption bandwidth of 10.27 GHz were achieved with a filler content as low as 30 wt.%.
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710129, Shaanxi, China.
* Correspondence to: Prof. Wangchang Geng, Prof. Panbo Liu, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical
University, Xi’an 710129, Shaanxi, China. E-mail: w.geng@nwpu.edu.cn; liupanbo@nwpu.edu.cn
www.oaepublish.com Submit a Manuscript: https://ucenter.oaepublish.com