Page 108 - Read Online
P. 108
Huang et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 24 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.07 Page 15 of 19
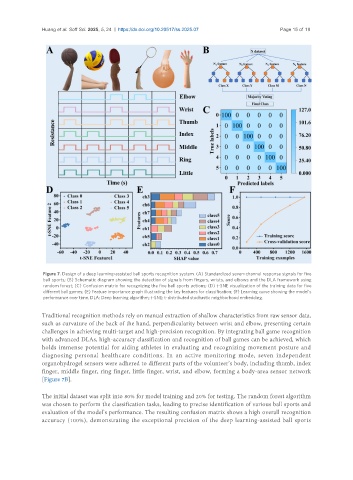
Figure 7. Design of a deep learning-assisted ball sports recognition system. (A) Standardized seven-channel response signals for five
ball sports; (B) Schematic diagram showing the detection of signals from fingers, wrists, and elbows and the DLA framework using
random forest; (C) Confusion matrix for recognizing the five ball sports actions; (D) t-SNE visualization of the training data for five
different ball games; (E) Feature importance graph illustrating the key features for classification; (F) Learning curve showing the model’s
performance over time. DLA: Deep learning algorithm; t-SNE: t-distributed stochastic neighborhood embedding.
Traditional recognition methods rely on manual extraction of shallow characteristics from raw sensor data,
such as curvature of the back of the hand, perpendicularity between wrist and elbow, presenting certain
challenges in achieving multi-target and high-precision recognition. By integrating ball game recognition
with advanced DLAs, high-accuracy classification and recognition of ball games can be achieved, which
holds immense potential for aiding athletes in evaluating and recognizing movement posture and
diagnosing personal healthcare conditions. In an active monitoring mode, seven independent
organohydrogel sensors were adhered to different parts of the volunteer’s body, including thumb, index
finger, middle finger, ring finger, little finger, wrist, and elbow, forming a body-area sensor network
[Figure 7B].
The initial dataset was split into 80% for model training and 20% for testing. The random forest algorithm
was chosen to perform the classification tasks, leading to precise identification of various ball sports and
evaluation of the model’s performance. The resulting confusion matrix shows a high overall recognition
accuracy (100%), demonstrating the exceptional precision of the deep learning-assisted ball sports