Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Wang et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:41 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.53 Page 29 of 43
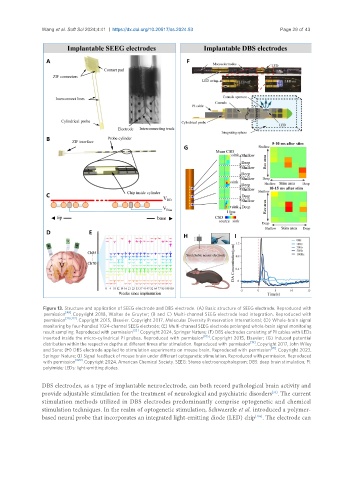
Figure 13. Structure and application of SEEG electrode and DBS electrode. (A) Basic structure of SEEG electrode. Reproduced with
[49]
permission . Copyright 2018, Walter de Gruyter; (B and C) Multi-channel SEEG electrode lead integration. Reproduced with
[216,217]
permission . Copyright 2015, Elsevier. Copyright 2017, Molecular Diversity Preservation International; (D) Whole-brain signal
monitoring by four-handled 1024-channel SEEG electrode; (E) Multi-channel SEEG electrode prolonged whole-brain signal monitoring
[32]
result sampling. Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2024, Springer Nature; (F) DBS electrodes consisting of PI cables with LEDs
inserted inside the micro-cylindrical PI probes. Reproduced with permission [105] . Copyright 2015, Elsevier; (G) Induced potential
distribution within the respective depths at different times after stimulation. Reproduced with permission [19] . Copyright 2017, John Wiley
and Sons; (H) DBS electrode applied to stimulation experiments on mouse brain. Reproduced with permission [95] . Copyright 2023,
Springer Nature; (I) Signal feedback of mouse brain under different optogenetic stimulation. Reproduced with permission. Reproduced
with permission [220] . Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. SEEG: Stereo electroencephalogram; DBS: deep brain stimulation; PI:
polyimide; LEDs: light-emitting diodes.
DBS electrodes, as a type of implantable neuroelectrode, can both record pathological brain activity and
provide adjustable stimulation for the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders . The current
[33]
stimulation methods utilized in DBS electrodes predominantly comprise optogenetic and chemical
stimulation techniques. In the realm of optogenetic stimulation, Schwaerzle et al. introduced a polymer-
based neural probe that incorporates an integrated light-emitting diode (LED) chip . The electrode can
[105]