Page 67 - Read Online
P. 67
Wu et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:29 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.21 Page 13 of 22
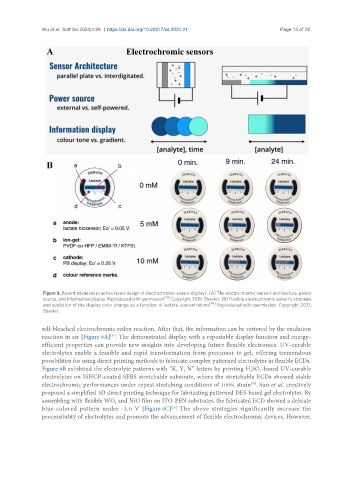
Figure 8. Recent advances in active layers design in electrochromic sensor displays. (A) The electrochromic sensors architecture, power
source, and information display. Reproduced with permission [111] . Copyright 2019, Elsevier; (B) Flexible electrochromic sensor’s structure
and evolution of the display color change as a function of lactate concentrations [60] . Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2021,
Elsevier.
self-bleached electrochromic redox reaction. After that, the information can be restored by the oxidation
reaction in air [Figure 9A] . The demonstrated display with a repeatable display function and energy-
[21]
efficient properties can provide new insights into developing future flexible electronics. UV-curable
electrolytes enable a feasible and rapid transformation from precursor to gel, offering tremendous
possibilities for using direct printing methods to fabricate complex patterned electrolytes in flexible ECDs.
Figure 9B exhibited the electrolyte patterns with “K, Y, N” letters by printing H SO -based UV-curable
2
4
electrolytes on ISHCP-coated SEBS stretchable substrate, where the stretchable ECDs showed stable
electrochromic performances under repeat stretching conditions of 100% strain . Sun et al. creatively
[50]
proposed a simplified 3D direct printing technique for fabricating patterned DES-based gel electrolytes. By
assembling with flexible WO and NiO film on ITO-PEN substrates, the fabricated ECD showed a delicate
3
blue-colored pattern under -3.0 V [Figure 9C] . The above strategies significantly increase the
[20]
processibility of electrolytes and promote the advancement of flexible electrochromic devices. However,