Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Park et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:28 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.22 Page 11 of 28
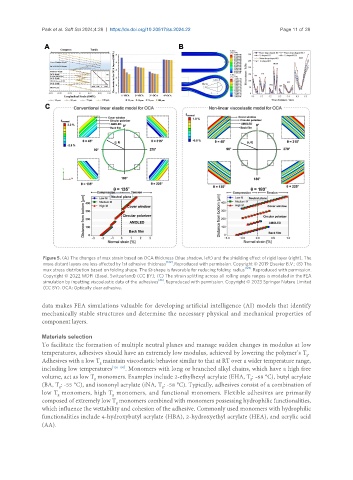
Figure 5. (A) The changes of max strain based on OCA thickness (blue shadow, left) and the shielding effect of rigid layer (right). The
more distant layers are less affected by 1st adhesive thickness [122] . Reproduced with permission. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V.; (B) The
max stress distribution based on folding shape. The Ω-shape is favorable for reducing folding radius [123] . Reproduced with permission.
Copyright © 2022 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) (CC BY); (C) The strain splitting across all rolling angle ranges is modeled in the FEA
simulation by inputting viscoelastic data of the adhesives [26] . Reproduced with permission. Copyright © 2023 Springer Nature Limited
(CC BY). OCA: Optically clear adhesive.
data makes FEA simulations valuable for developing artificial intelligence (AI) models that identify
mechanically stable structures and determine the necessary physical and mechanical properties of
component layers.
Materials selection
To facilitate the formation of multiple neutral planes and manage sudden changes in modulus at low
temperatures, adhesives should have an extremely low modulus, achieved by lowering the polymer’s T .
g
Adhesives with a low T maintain viscoelastic behavior similar to that at RT over a wider temperature range,
g
including low temperatures [126-130] . Monomers with long or branched alkyl chains, which have a high free
volume, act as low T monomers. Examples include 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (EHA, T : -68 °C), butyl acrylate
g
g
(BA, T : -55 °C), and isononyl acrylate (iNA, T : -58 °C). Typically, adhesives consist of a combination of
g
g
low T monomers, high T monomers, and functional monomers. Flexible adhesives are primarily
g
g
composed of extremely low T monomers combined with monomers possessing hydrophilic functionalities,
g
which influence the wettability and cohesion of the adhesive. Commonly used monomers with hydrophilic
functionalities include 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate (HBA), 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), and acrylic acid
(AA).