Page 163 - Read Online
P. 163
Page 24 of 31 Lee et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:38 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.36
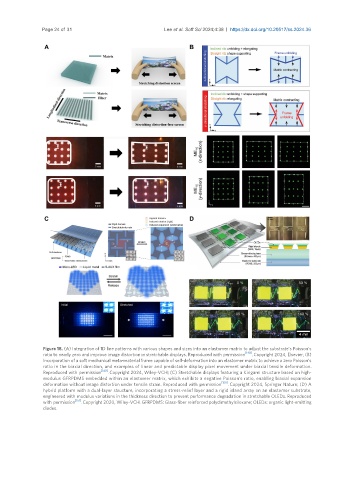
Figure 18. (A) Integration of 1D line patterns with various shapes and sizes into an elastomer matrix to adjust the substrate’s Poisson’s
[148]
ratio to nearly zero and improve image distortion in stretchable displays. Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2024, Elsevier; (B)
Incorporation of a soft mechanical meta-material frame capable of self-deformation into an elastomer matrix to achieve a zero Poisson’s
ratio in the biaxial direction, and examples of linear and predictable display pixel movement under biaxial tensile deformation.
[149]
Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH; (C) Stretchable displays featuring a Kirigami structure based on high-
modulus GFRPDMS embedded within an elastomer matrix, which exhibits a negative Poisson’s ratio, enabling biaxial expansion
deformation without image distortion under tensile strain. Reproduced with permission [150] . Copyright 2024, Springer Nature; (D) A
hybrid platform with a dual-layer structure, incorporating a stress-relief layer and a rigid island array on an elastomer substrate,
engineered with modulus variations in the thickness direction to prevent performance degradation in stretchable OLEDs. Reproduced
with permission [151] . Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. GFRPDMS: Glass-fiber reinforced polydimethylsiloxane; OLEDs: organic light-emitting
diodes.