Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Page 26 of 38 Zhu et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.05
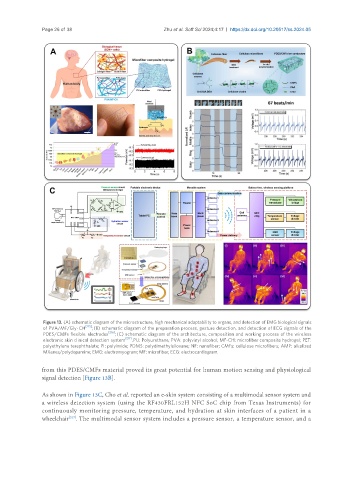
Figure 13. (A) schematic diagram of the microstructure, high mechanical adaptability to organs, and detection of EMG biological signals
of PVA/MF/Gly-CH [215] ; (B) schematic diagram of the preparation process, gesture detection, and detection of ECG signals of the
PDES/CMFs flexible electrodes [216] ; (C) schematic diagram of the architecture, composition and working process of the wireless
electronic skin clinical detection system [217] . PU: Polyurethane; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; MF-CH: microfiber composite hydrogel; PET:
polyethylene terephthalate; PI: polyimide; PDMS: polydimethylsiloxane; NF: nanofiber; CMFs: cellulose microfibers; AMP: alkalized
MXenes/polydopamine; EMG: electromyogram; MF: microfiber; ECG: electrocardiogram.
from this PDES/CMFs material proved its great potential for human motion sensing and physiological
signal detection [Figure 13B].
As shown in Figure 13C, Cho et al. reported an e-skin system consisting of a multimodal sensor system and
a wireless detection system (using the RF430FRL152H NFC SoC chip from Texas Instruments) for
continuously monitoring pressure, temperature, and hydration at skin interfaces of a patient in a
[217]
wheelchair . The multimodal sensor system includes a pressure sensor, a temperature sensor, and a