Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Page 24 of 38 Wei et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.09
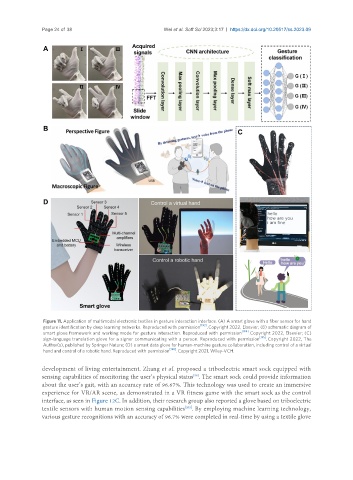
Figure 11. Application of multimodal electronic textiles in gesture interaction interface. (A) A smart glove with a fiber sensor for hand
gesture identification by deep learning networks. Reproduced with permission [193] . Copyright 2022, Elsevier; (B) schematic diagram of
smart glove framework and working mode for gesture interaction. Reproduced with permission [194] . Copyright 2022, Elsevier; (C)
sign-language translation glove for a signer communicating with a person. Reproduced with permission [195] . Copyright 2022, The
Author(s), published by Springer Nature; (D) a smart data glove for human-machine gesture collaboration, including control of a virtual
hand and control of a robotic hand. Reproduced with permission [196] . Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.
development of living entertainment. Zhang et al. proposed a triboelectric smart sock equipped with
sensing capabilities of monitoring the user’s physical status . The smart sock could provide information
[56]
about the user’s gait, with an accuracy rate of 96.67%. This technology was used to create an immersive
experience for VR/AR scene, as demonstrated in a VR fitness game with the smart sock as the control
interface, as seen in Figure 12C. In addition, their research group also reported a glove based on triboelectric
textile sensors with human motion sensing capabilities . By employing machine learning technology,
[205]
various gesture recognitions with an accuracy of 96.7% were completed in real-time by using a textile glove