Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Jung et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.02 Page 15 of 44
+
+
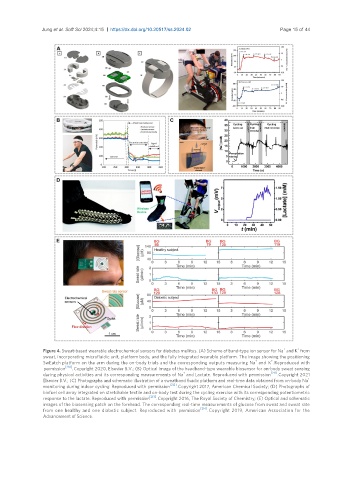
Figure 4. Sweat-based wearable electrochemical sensors for diabetes mellitus. (A) Scheme of band-type ion sensor for Na and K from
sweat, incorporating microfluidic unit, platform body, and the fully integrated wearable platform. The image showing the positioning
+
+
SwEatch platform on the arm during the on-body trials and the corresponding outputs measuring Na and K . Reproduced with
permission [210] . Copyright 2020, Elsevier B.V.; (B) Optical image of the headband-type wearable biosensor for on-body sweat sensing
+
during physical activities and its corresponding measurements of Na and Lactate. Reproduced with permission [211] . Copyright 2021
+
Elsevier B.V.; (C) Photographs and schematic illustration of a sweatband fluidic platform and real-time data obtained from on-body Na
monitoring during indoor cycling. Reproduced with permission [212] . Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (D) Photographs of
biofuel cell array integrated on stretchable textile and on-body test during the cycling exercise with its corresponding potentiometric
response to the lactate. Reproduced with permission [213] . Copyright 2016, The Royal Society of Chemistry; (E) Optical and schematic
images of the biosensing patch on the forehead. The corresponding real-time measurements of glucose from sweat and sweat rate
[214]
from one healthy and one diabetic subject. Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2019, American Association for the
Advancement of Science.