Page 41 - Read Online
P. 41
Page 20 of 44 Jung et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.02
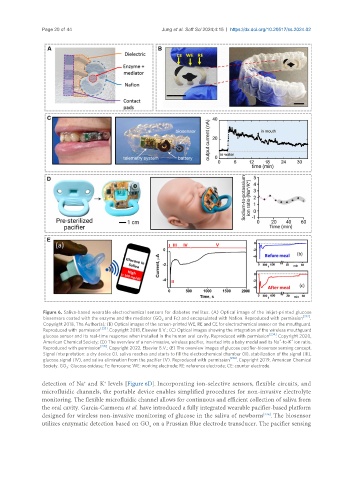
Figure 6. Saliva-based wearable electrochemical sensors for diabetes mellitus. (A) Optical image of the inkjet-printed glucose
biosensors coated with the enzyme and the mediator (GO and Fc) and encapsulated with Nafion. Reproduced with permission [232] .
X
Copyright 2018, The Author(s); (B) Optical images of the screen-printed WE, RE and CE for electrochemical sensor on the mouthguard.
Reproduced with permission [233] . Copyright 2018, Elsevier B.V.; (C) Optical images showing the integration of the wireless mouthguard
glucose sensor and its real-time response when installed in the human oral cavity. Reproduced with permission [234] . Copyright 2020,
+
+
American Chemical Society; (D) The overview of a non-invasive, wireless pacifier, inserted into a baby model and its Na -to-K ion ratio.
Reproduced with permission [235] . Copyright 2022, Elsevier B.V.; (E) The overview images of glucose pacifier-biosensor sensing concept.
Signal interpretation: a dry device (I), saliva reaches and starts to fill the electrochemical chamber (II), stabilization of the signal (III),
glucose signal (IV), and saliva elimination from the pacifier (V). Reproduced with permission [236] . Copyright 2019, American Chemical
Society. GO : Glucose oxidase; Fc: ferrocene; WE: working electrode; RE: reference electrode; CE: counter electrode.
X
detection of Na and K levels [Figure 6D]. Incorporating ion-selective sensors, flexible circuits, and
+
+
microfluidic channels, the portable device enables simplified procedures for non-invasive electrolyte
monitoring. The flexible microfluidic channel allows for continuous and efficient collection of saliva from
the oral cavity. Garcia-Carmona et al. have introduced a fully integrated wearable pacifier-based platform
[236]
designed for wireless non-invasive monitoring of glucose in the saliva of newborns . The biosensor
utilizes enzymatic detection based on GO on a Prussian Blue electrode transducer. The pacifier sensing
x