Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Hwang et al. In vivo degradation of PLDLA-TMC
A Auto-scaled chromatogram A 1.00
80.00
70.00
0.95
60.00
50.00
0.90
40.00
MV 30.00
20.00 0.85
10.00
0.00
0.80
-10.00
-20.00
5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 40.00 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000
B Minutes B
Auto-scaled chromatogram
80.00 1.00
70.00
60.00
0.95
50.00
40.00
0.90
MV 30.00
20.00
10.00
0.85
0.00
-10.00
-20.00 0.80
5.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 25.00 30.00 35.00 40.00
Minutes 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000
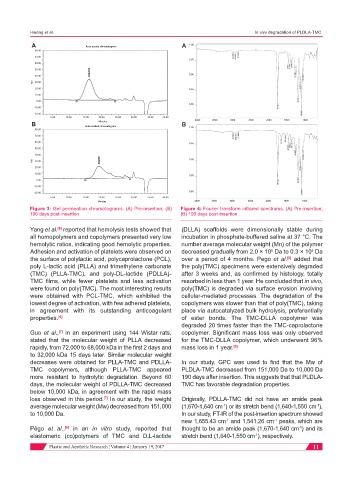
Figure 3: Gel permeation chromatograms. (A) Pre-insertion; (B) Figure 4: Fourier transform infrared spectrums. (A) Pre-insertion;
190 days post-insertion (B) 190 days post-insertion
Yang et al. reported that hemolysis tests showed that (DLLA) scaffolds were dimensionally stable during
[6]
all homopolymers and copolymers presented very low incubation in phosphate-buffered saline at 37 °C. The
hemolytic ratios, indicating good hemolytic properties. number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer
Adhesion and activation of platelets were observed on decreased gradually from 2.0 × 10 Da to 0.3 × 10 Da
5
5
the surface of polylactic acid, polycaprolactone (PCL), over a period of 4 months. Pego et al. added that
[8]
poly L-lactic acid (PLLA) and trimethylene carbonate the poly(TMC) specimens were extensively degraded
(TMC) (PLLA-TMC), and poly-DL-lactide (PDLLA)- after 3 weeks and, as confirmed by histology, totally
TMC films, while fewer platelets and less activation resorbed in less than 1 year. He concluded that in vivo,
were found on poly(TMC). The most interesting results poly(TMC) is degraded via surface erosion involving
were obtained with PCL-TMC, which exhibited the cellular-mediated processes. The degradation of the
lowest degree of activation, with few adhered platelets, copolymers was slower than that of poly(TMC), taking
in agreement with its outstanding anticoagulant place via autocatalyzed bulk hydrolysis, preferentially
properties. [6] of ester bonds. The TMC-DLLA copolymer was
degraded 20 times faster than the TMC-caprolactone
Guo et al., in an experiment using 144 Wistar rats, copolymer. Significant mass loss was only observed
[7]
stated that the molecular weight of PLLA decreased for the TMC-DLLA copolymer, which underwent 96%
rapidly, from 72,000 to 68,000 kDa in the first 2 days and mass loss in 1 year. [9]
to 32,000 kDa 15 days later. Similar molecular weight
decreases were obtained for PLLA-TMC and PDLLA- In our study, GPC was used to find that the Mw of
TMC copolymers, although PLLA-TMC appeared PLDLA-TMC decreased from 151,000 Da to 10,000 Da
more resistant to hydrolytic degradation. Beyond 60 190 days after insertion. This suggests that that PLDLA-
days, the molecular weight of PDLLA-TMC decreased TMC has favorable degradation properties.
below 10,000 kDa, in agreement with the rapid mass
[7]
loss observed in this period. In our study, the weight Originally, PDLLA-TMC did not have an amide peak
average molecular weight (Mw) decreased from 151,000 (1,670-1,640 cm ) or its stretch bend (1,640-1,550 cm ).
-1
-1
to 10,000 Da. In our study, FT-IR of the post-insertion spectrum showed
new 1,655.43 cm and 1,541.26 cm peaks, which are
-1
-1
Pêgo et al., in an in vitro study, reported that thought to be an amide peak (1,670-1,640 cm ) and its
-1
[8]
elastomeric (co)polymers of TMC and D,L-lactide stretch bend (1,640-1,550 cm ), respectively.
-1
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ January 19, 2017 11