Page 119 - Read Online
P. 119
Khan Volume difference management in asymmetrical breasts
Table 6: Over all mean tissue resection from each side resection from larger breast or having same amount
in group C, as well as respective mean tissue resection of tissue reduced from both sides with different size
from each breast when breast were larger on either implants. There is an advantage of asymmetrical
right (C1) or left side (C2) breast tissue reduction and use of same size implants.
Right breast Left breast P value In case, a patient gains or loses weight in future, breast
Average tissue resection 114 ± 172.1 124 ± 107.8 0.835 volume is likely to go up or down in similar proportions
from asymmetrical breasts
(n = 18) without reintroducing asymmetry. However when
More tissue resected from 276 ± 265.9 181 ± 185.8 0.530 two different size implants are used leaving original
right bigger breast (group breast asymmetry unaddressed, patient’s weight
C1, n = 7) changes may accentuate original breast volumetric
More tissue resected from 49 ± 24.5 105 ± 44.6 0.001 differences. The use of fixed-volume implants for
left bigger breasts (group
C2, n = 11) asymmetry correction has shown low revision rate. [14-17]
Other commonly used options are adjustable breast
studies did not include details for volume difference implants or intraoperative sizers. [18,19] In more complex
management in asymmetrical breasts even though the deformities, more complex surgical procedures are
most common reason for implant related revision noted required. [20]
was change of size of implant. [9,10] A good interactive
process of preoperative sizing for implants is effective Analysis of the current study has shown some
and can avoid revisional surgery. [11,12] A more rigid interesting results. In group A that required asymmetry
high five or more scientific and accurate way is to use correction using different size implants only, out of
3-D photography combined with measurements of 240 patients, 145 (60%) breasts were larger on the
patients. [5,13] However a rigid five point system or 3-D left showing a relative predisposition of left side to be
photography without patient’s participation can leave larger as reported in earlier studies. [4,14] When different
the subject unhappy. In author’s practice, a trial of fixed sizes implants were used on two sides in group A (A1
volume implants in a desired size brassiere is practical and A2) and compared with the size of the implants
and effective and revision rates of less than 1% was used in symmetrical breasts, there was no statistical
reported. [14] After carrying out a careful examination difference between the sizes of implants used in
of chest, breast and tissue characteristics, different each group [Table 2]. However when the implants
size and profile implants are placed in a desired size sizes were compared on two sides in patients with
bra until surgeon and patients agree on the size and asymmetry, the difference in breast implant sizes was
symmetry of breasts. Those who presents with breast significant [Table 3]. Also, when the right breast is
asymmetry with ptosis, patients are given the choice larger, the difference is likely to be more noticeable
to have either similar size implants with more tissue requiring larger average volume for correction on
A B C
D E F
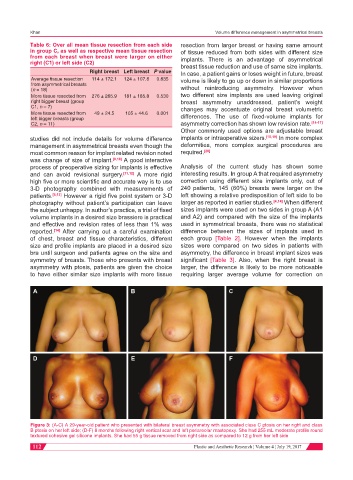
Figure 3: (A-C) A 29-year-old patient who presented with bilateral breast asymmetry with associated class C ptosis on her right and class
B ptosis on her left side; (D-F) 8 months following right vertical scar and left periareolar mastopexy. She had 255 mL moderate profile round
textured cohesive gel silicone implants. She had 55 g tissue removed from right side as compared to 12 g from her left side
112 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ July 19, 2017