Page 118 - Read Online
P. 118
Khan Volume difference management in asymmetrical breasts
Table 4: Comparison of average size implants used in Table 5: Comparative analysis and relative distribution
symmetrical breasts with ptosis and that of average of different size implants used in asymmetrical breasts
size implants used in asymmetrical breasts requiring with ptosis (group B1 and B2)
mastopexy with different size implants with same Larger implant used on
volume tissue reduction (group B) P value
Right (mL) Left (mL)
Symmetrical breasts Asymmetrical P Group B1 (n = 7) 334 ± 52.2 270 ± 42.7 0.027
with ptosis (n = 117) breasts with ptosis value Group B2 (n = 13) 297 ± 82.1 377 ± 102.4 0.037
Average size of implants
used on right (n = 20)
Range (mL) 170-800 200-495 Statistical analysis was significant on two sides (P =
Mean ± SD 302 ± 87.1 314 ± 75.1 0.563 0.001) [Table 6].
Same size implants Average size of implants
(n = 117) used on left (n = 20)
Range (mL) 170-800 200-615 DISCUSSION
Mean ± SD 302 ± 87.1 339 ± 99.7 0.088
Chest and breast asymmetries are very common and
from one of the two sides for breast volume asymmetry its prevalence has been reported in retrospective and
[1-4]
correction (> 20 g). Mean tissue excised from right prospective studies. The reported incidence of
side was 114.0 ± 172.1 g as compared to 124.0 ± prospective clinical examination showed volume and
107.8 g on the left. There was no statistical difference nipple areolar level difference of 46.6% and 32.6%
[4]
between the tissues removed from two sides (P = respectively and were significantly noticeable on left.
0.835) [Figures 3 and 4]. Chest and breast asymmetries were also noted in
88% of patients and a combination of manual and
[3]
The group was further subdivided in C1 and C2. 3D photography showed 81.7% soft tissue volumetric
Subgroup C1 included 7 patients who had larger differences and when these soft differences were
breasts on right side and had more tissue removed combined with chest bony asymmetries, incidences
[5]
from their right side (> 20 g). Mean weight of tissue of asymmetry rose to 100%. Another commonly
excised from the right side was 276.0 ± 265.9 g as overlooked asymmetry is asymmetrically placed nipple
[6]
compared to 181.0 ±185.8 g on left side. There was areolar complex in horizontal axis. However none of
no statistical difference on the breast tissue removed the above studies gave details of volume difference
from two sides in this group (P = 0.530). Subgroup management. [3-6]
C2 included 11 patients who had larger breast on left
and more tissue excised from left side. In this group Augmentation mammoplasty when performed alone or
mean weight of the tissue removed from left side was as a single stage breast augmentation with mastopexy
105.0 ± 44.6 g as compared to 49.0 ± 24.5 g on right. has shown an acceptable results. [7-9] However,
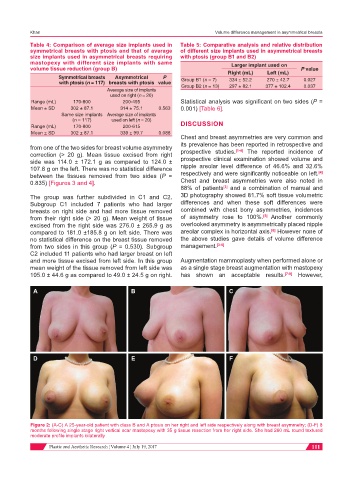
A B C
D E F
Figure 2: (A-C) A 25-year-old patient with class B and A ptosis on her right and left side respectively along with breast asymmetry; (D-F) 8
months following single stage right vertical scar mastopexy with 35 g tissue resection from her right side. She had 260 mL round textured
moderate profile implants bilaterally
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ July 19, 2017 111