Page 382 - Read Online
P. 382
Fang et al. Negative pressure wound therapy for diabetic foot limb salvage
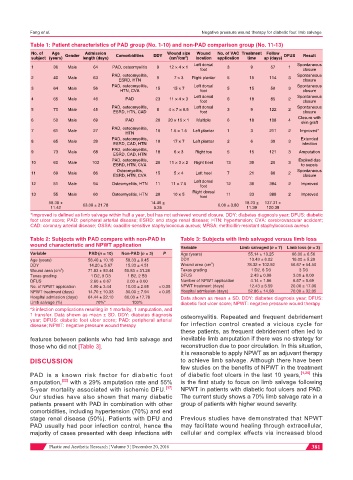
Table 1: Patient characteristics of PAD group (No. 1-10) and non-PAD comparison group (No. 11-13)
No. of Age Gender Admission Comorbidities DDY Wound size Wound No. of VAC Treatment Follow DFUS Result
3
subject (years) length (days) (cm /cm ) 2 location application time up (days)
Left dorsal Spontaneous
1 36 Male 64 PAD, osteomyelitis 9 12 × 4 × 1 3 9 57 1
foot closure
PAD, osteomyelitis, Spontaneous
2 40 Male 63 9 7 × 3 Right plantar 5 15 114 3
ESRD, HTN closure
PAD, osteomyelitis, Left dorsal Spontaneous
3 64 Male 56 15 15 × 7 5 15 50 3
HTN, CVA foot closure
Left dorsal Spontaneous
4 65 Male 46 PAD 23 11 × 4 × 3 6 18 85 2
foot closure
PAD, osteomyelitis, Left dorsal Spontaneous
5 70 Male 45 8 4 × 7 × 0.5 3 9 122 2
ESRD, HTN, CAD foot closure
Closure with
6 50 Male 69 PAD 20 20 × 15 × 1 Multiple 6 18 108 4 skin graft
PAD, osteomyelitis,
7 61 Male 27 10 1.5 × 1.5 Left plantar 1 3 211 2 Improved*
HTN
PAD, osteomyelitis, Extended
8 65 Male 39 10 17 × 7 Left plantar 2 6 39 3
ESRD, CAD, HTN infection
PAD, osteomyelitis,
9 73 Male 68 18 6 × 3 Right toe 5 15 121 3 Amputation
ESRD, CAD, HTN
PAD, osteomyelitis, Expired due
10 60 Male 103 20 11 × 3 × 2 Right heel 13 39 20 3
ESRD, HTN, CVA to sepsis
Osteomyelitis, Spontaneous
11 69 Male 86 15 5 × 4 Left heel 7 21 86 2
ESRD, HTN, CVA closure
Left dorsal
12 51 Male 94 Osteomyelitis, HTN 11 11 × 7.5 12 36 384 2 Improved
foot
Right dorsal
13 55 Male 60 Osteomyelitis, HTN 20 10 × 5 11 33 388 2 Improved
foot
58.38 ± 63.08 ± 21.78 14.46 ± 6.08 ± 3.80 18.23 ± 137.31 ±
11.42 5.25 11.39 120.38
*Improved is defined as limb salvage within half a year, but has not achieved wound closure. DDY: diabetes diagnosis year; DFUS: diabetic
foot ulcer score; PAD: peripheral arterial disease; ESRD: end stage renal disease; HTN: hypertension; CVA: cerebrovascular accident;
CAD: coronary arterial disease; OSSA: oxacillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus; MRSA: methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
Table 2: Subjects with PAD compare with non-PAD in Table 3: Subjects with limb salvaged versus limb loss
wound characteristic and NPWT application
Variable Limb salvaged (n = 7) Limb loss (n = 3)
Variable PAD (n = 10) Non-PAD (n = 3) P Age (years) 55.14 ± 13.25 66.00 ± 6.56
Age (years) 58.40 ± 10.18 58.33 ± 9.45 DDY 13.43 ± 6.02 16.00 ± 5.29
2
DDY 14.20 ± 5.67 15.33 ± 4.51 Wound area (cm ) 78.32 ± 102.92 56.67 ± 54.50
Wound area (cm ) 2 71.83 ± 93.44 50.83 ± 31.26 Texas grading 1 D2, 6 D3 3 D3
Texas grading 1 D2, 9 D3 1 B2, 2 B3 DFUS 2.43 ± 0.98 3.00 ± 0.00
DFUS 2.60 ± 0.67 2.00 ± 0.00 Number of NPWT application 4.14 ± 1.86 6.67 ± 5.69
No. of NPWT application 4.90 ± 3.44 10.00 ± 2.65 < 0.05 NPWT treatment (days) 12.43 ± 5.59 20.00 ± 17.06
NPWT treatment (days) 14.70 ± 10.33 30.00 ± 7.94 < 0.05 Hospital admission (days) 52.86 ± 14.58 70.00 ± 32.05
Hospital admission (days) 64.44 ± 22.10 60.00 ± 17.78 Data shown as mean ± SD. DDY: diabetes diagnosis year; DFUS:
Limb salvage (%) 70%* 100% diabetic foot ulcer score; NPWT: negative pressure wound therapy
*3 infection complications resulting in 1 mortality, 1 amputation, and
1 transfer. Data shown as mean ± SD. DDY: diabetes diagnosis osteomyelitis. Repeated and frequent debridement
year; DFUS: diabetic foot ulcer score; PAD: peripheral arterial
disease; NPWT: negative pressure wound therapy for infection control created a vicious cycle for
these patients, as frequent debridement often led to
features between patients who had limb salvage and inevitable limb amputation if there was no strategy for
those who did not [Table 3]. reconstruction due to poor circulation. In this situation,
it is reasonable to apply NPWT as an adjuvant therapy
DISCUSSION to achieve limb salvage. Although there have been
few studies on the benefits of NPWT in the treatment
PAD is a known risk factor for diabetic foot of diabetic foot ulcers in the last 10 years, [1,20] this
amputation, [22] with a 29% amputation rate and 55% is the first study to focus on limb salvage following
5-year mortality associated with ischemic DFU. [17] NPWT in patients with diabetic foot ulcers and PAD.
Our studies have also shown that many diabetic The current study shows a 70% limb salvage rate in a
patients present with PAD in combination with other group of patients with higher wound severity.
comorbidities, including hypertension (70%) and end
stage renal disease (50%). Patients with DFU and Previous studies have demonstrated that NPWT
PAD usually had poor infection control, hence the may facilitate wound healing through extracellular,
majority of cases presented with deep infections with cellular and complex effects via increased blood
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 20, 2016 381