Page 338 - Read Online
P. 338
Sharma et al. Morel-Lavalle lesion
A B C
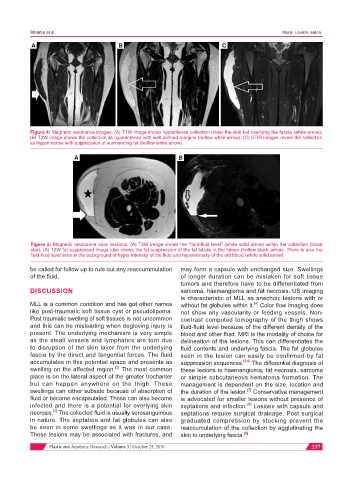
Figure 4: Magnetic resonance images. (A) T1W image shows hypointense collection under the skin but overlying the fascia (white arrow);
(B) T2W image shows the collection as hyperintense with well defined margins (hollow white arrow); (C) STIR images reveal the collection
as hyperintense with suppression of surrounding fat (hollow white arrow)
A B
Figure 5: Magnetic resonance axial sections. (A) T2W image shows the “fluid-fluid level” (white solid arrow) within the collection (black
star); (B) T2W fat suppressed image also shows the fat suppression of the fat lobule in the lumen (hollow black arrow). There is also the
fluid-fluid level seen in the background of hyper intensity of the fluid and hypointensity of the old blood (white solid arrow)
be called for follow up to rule out any reaccummulation may form a capsule with unchanged size. Swellings
of the fluid. of longer duration can be mistaken for soft tissue
tumors and therefore have to be differentiated from
DISCUSSION sarcoma, haemangioma and fat necrosis. US imaging
is characteristic of MLL as anechoic lesions with or
MLL is a common condition and has got other names without fat globules within it. Color flow imaging does
[4]
like post-traumatic soft tissue cyst or pseudolipoma. not show any vascularity or feeding vessels. Non-
Post traumatic swelling of soft tissues is not uncommon contrast computed tomography of the thigh shows
and this can be misleading when degloving injury is fluid-fluid level because of the different density of the
present. The underlying mechanism is very simple blood and other fluid. MRI is the modality of choice for
as the small vessels and lymphatics are torn due delineation of the lesions. This can differentiates the
to disruption of the skin layer from the underlying fluid contents and underlying fascia. The fat globules
fascia by the direct and tangential forces. The fluid seen in the lesion can easily be confirmed by fat
accumulates in this potential space and presents as suppression sequences. [5,6] The differential diagnosis of
swelling on the affected region. The most common these lesions is haemangioma, fat necrosis, sarcoma
[2]
place is on the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter or simple subcutaneous hematoma formation. The
but can happen anywhere on the thigh. These management is dependent on the size, location and
swellings can either subside because of absorption of the duration of the lesion. Conservative management
[7]
fluid or become encapsulated. These can also become is advocated for smaller lesions without presence of
infected and there is a potential for overlying skin septations and infection. Lesions with capsule and
[8]
[3]
necrosis. The collected fluid is usually serosanguinous septations require surgical drainage. Post surgical
in nature. The septation and fat globules can also graduated compression by stocking prevent the
be seen in some swellings as it was in our case. reaccumulation of the collection by agglutinating the
These lesions may be associated with fractures, and skin to underlying fascia. [9]
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 25, 2016 337