Page 343 - Read Online
P. 343
Haffner The temporal endoscopic midface lift
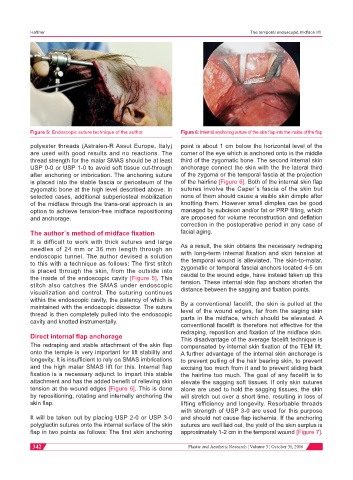
Figure 5: Endoscopic suture technique of the author Figure 6: Internal anchoring suture of the skin flap into the inside of the flap
polyester threads (Astralen-R Assut Europe, Italy) point is about 1 cm below the horizontal level of the
are used with good results and no reactions. The corner of the eye which is anchored onto in the middle
thread strength for the malar SMAS should be at least third of the zygomatic bone. The second internal skin
USP 0-0 or USP 1-0 to avoid soft tissue cut-through anchorage connect the skin with the the lateral third
after anchoring or imbrication. The anchoring suture of the zygoma or the temporal fascia at the projection
is placed into the stable fascia or periosteum of the of the hairline [Figure 6]. Both of the internal skin flap
zygomatic bone at the high level described above. In sutures involve the Caper´s fascia of the skin but
selected cases, additional subperiosteal mobilization none of them should cause a visible skin dimple after
of the midface through the trans-oral approach is an knotting them. However small dimples can be good
option to achieve tension-free midface repositioning managed by subcision and/or fat or PRP filling, which
and anchorage. are proposed for volume reconstruction and deflation
correction in the postoperative period in any case of
The author´s method of midface fixation facial aging.
It is difficult to work with thick sutures and large
needles of 24 mm or 36 mm length through an As a result, the skin obtains the necessary redraping
with long-term internal fixation and skin tension at
endoscopic tunnel. The author devised a solution
to this with a technique as follows: The first stitch the temporal wound is alleviated. The skin-to-malar,
is placed through the skin, from the outside into zygomatic or temporal fascial anchors located 4-5 cm
the inside of the endoscopic cavity [Figure 5]. This caudal to the wound edge, have instead taken up this
stitch also catches the SMAS under endoscopic tension. These internal skin flap anchors shorten the
distance between the sagging and fixation points.
visualization and control. The suturing continues
within the endoscopic cavity, the patency of which is
maintained with the endoscopic dissector. The suture By a conventional facelift, the skin is pulled at the
thread is then completely pulled into the endoscopic level of the wound edges, far from the saging skin
cavity and knotted instrumentally. parts in the midface, which should be elevated. A
conventional facelift is therefore not effective for the
redraping, reposition and fixation of the midface skin.
Direct internal flap anchorage This disadvantage of the average facelift technique is
The redraping and stable attachment of the skin flap compensated by internal skin fixation of the TEM lift.
onto the temple is very important for lift stability and A further advantage of the internal skin anchorage is
longevity. It is insufficient to rely on SMAS imbrications to prevent pulling of the hair bearing skin, to prevent
and the high malar SMAS lift for this. Internal flap excising too much from it and to prevent sliding back
fixation is a necessary adjunct to impart this stable the hairline too much. The goal of any facelift is to
attachment and has the added benefit of relieving skin elevate the sagging soft tissues. If only skin sutures
tension at the wound edges [Figure 6]. This is done alone are used to hold the sagging tissues, the skin
by repositioning, rotating and internally anchoring the will stretch out over a short time, resulting in loss of
skin flap. lifting efficiency and longevity. Resorbable threads
with strength of USP 3-0 are used for this purpose
It will be taken out by placing USP 2-0 or USP 3-0 and should not cause flap ischemia. If the anchoring
polyglactin sutures onto the internal surface of the skin sutures are well laid out, the yield of the skin surplus is
flap in two points as follows: The first skin anchoring approximately 1-2 cm in the temporal wound [Figure 7].
342 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 31, 2016