Page 274 - Read Online
P. 274
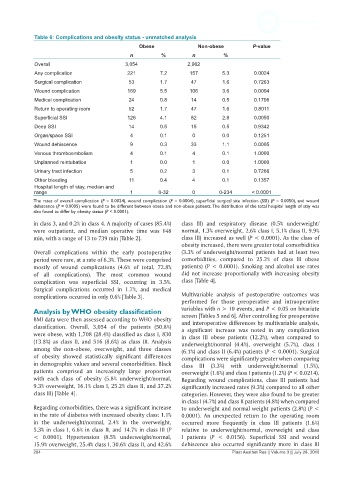
Table 6: Complications and obesity status - unmatched analysis
Obese Non-obese P-value
n % n %
Overall 3,054 2,962
Any complication 221 7.2 157 5.3 0.0024
Surgical complication 53 1.7 47 1.6 0.7263
Wound complication 169 5.5 106 3.6 0.0004
Medical complication 24 0.8 14 0.5 0.1706
Return to operating room 52 1.7 47 1.6 0.8011
Superficial SSI 126 4.1 82 2.8 0.0050
Deep SSI 14 0.5 15 0.5 0.9342
Organ/space SSI 4 0.1 0 0.0 0.1251
Wound dehiscence 9 0.3 33 1.1 0.0005
Venous thromboembolism 4 0.1 4 0.1 1.0000
Unplanned reintubation 1 0.0 1 0.0 1.0000
Urinary tract infection 5 0.2 3 0.1 0.7266
Other bleeding 11 0.4 4 0.1 0.1357
Hospital length of stay, median and
range 1 0-32 0 0-234 < 0.0001
The rates of overall complication (P = 0.0024), wound complication (P = 0.0004), superficial surgical site infection (SSI) (P = 0.0050), and wound
dehiscence (P = 0.0005) were found to be different between obese and non-obese patients. The distribution of the total hospital length of stay was
also found to differ by obesity status (P < 0.0001).
in class 3, and 0.2% in class 4. A majority of cases (85.4%) class III) and respiratory disease (0.5% underweight/
were outpatient, and median operative time was 148 normal, 1.3% overweight, 2.6% class I, 5.1% class II, 9.9%
min, with a range of 13 to 739 min [Table 2]. class III) increased as well (P < 0.0001). As the class of
obesity increased, there were greater total comorbidities
Overall complications within the early postoperative (3.3% of underweight/normal patients had at least two
period were rare, at a rate of 6.3%. These were comprised comorbidities, compared to 25.2% of class III obese
mostly of wound complications (4.6% of total, 72.8% patients) (P < 0.0001). Smoking and alcohol use rates
of all complications). The most common wound did not increase proportionally with increasing obesity
complication was superficial SSI, occurring in 3.5%. class [Table 4].
Surgical complications occurred in 1.7%, and medical
complications occurred in only 0.6% [Table 3]. Multivariable analysis of postoperative outcomes was
performed for those preoperative and intraoperative
Analysis by WHO obesity classification variables with n > 10 events, and P < 0.05 on bivariate
BMI data were then assessed according to WHO obesity screen [Tables 5 and 6]. After controlling for preoperative
and interoperative differences by multivariable analysis,
classification. Overall, 3,054 of the patients (50.8%) a significant increase was noted in any complication
were obese, with 1,708 (28.4%) classified as class I, 830 in class III obese patients (12.2%), when compared to
(13.8%) as class II, and 516 (8.6%) as class III. Analysis underweight/normal (4.4%), overweight (5.7%), class I
among the non-obese, overweight, and three classes (6.1%) and class II (6.4%) patients (P < 0.0001). Surgical
of obesity showed statistically significant differences complications were significantly greater when comparing
in demographic values and several comorbidities. Black class III (3.3%) with underweight/normal (1.5%),
patients comprised an increasingly large proportion overweight (1.6%) and class I patients (1.2%) (P < 0.0214).
with each class of obesity (5.8% underweight/normal, Regarding wound complications, class III patients had
9.3% overweight, 16.1% class I, 25.2% class II, and 37.2% significantly increased rates (9.3%) compared to all other
class III) [Table 4]. categories. However, they were also found to be greater
in class I (4.7%) and class II patients (4.8%) when compared
Regarding comorbidities, there was a significant increase to underweight and normal weight patients (2.8%) (P <
in the rate of diabetes with increased obesity class: 1.1% 0.0001). An unexpected return to the operating room
in the underweight/normal, 2.4% in the overweight, occurred more frequently in class III patients (1.6%)
5.3% in class I, 6.6% in class II, and 14.7% in class III (P relative to underweight/normal, overweight and class
< 0.0001). Hypertension (8.5% underweight/normal, I patients (P < 0.0156). Superficial SSI and wound
15.9% overweight, 25.4% class I, 30.6% class II, and 42.6% dehiscence also occurred significantly more in class III
264 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || July 28, 2016