Page 60 - Read Online
P. 60
a b
c
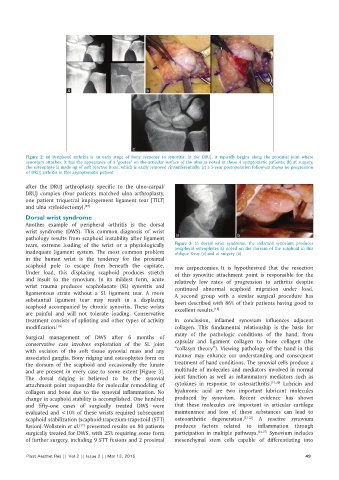
Figure 2: (a) Peripheral arthritis is an early stage of bone response to synovitis. In the DRUJ, it typically begins along the proximal joint where
synovium attaches. It has the appearance of a "goatee" on the articular surface of the ulna as noted in these 4 symptomatic patients; (b) at surgery,
the osteophyte is made up of soft reactive bone, which is easily removed circumferentially; (c) a 5-year postoperation follow‑up shows no progression
of DRUJ arthritis in this asymptomatic patient
after the DRUJ arthroplasty specific to the ulno‑carpal/
DRUJ complex (four patients matched ulna arthroplasty,
one patient triquetral impingement ligament tear [TILT]
and ulna styloidectomy). [15]
Dorsal wrist syndrome
Another example of peripheral arthritis is the dorsal
wrist syndrome (DWS). This common diagnosis of wrist a
pathology results from scaphoid instability after ligament b
tears, extreme loading of the wrist or a physiologically Figure 3: In dorsal wrist syndrome, the inflamed synovium produces
inadequate ligament system. The most common problem peripheral osteophytes as noted on the dorsum of the scaphoid in this
oblique X‑ray (a) and at surgery (b)
in the human wrist is the tendency for the proximal
scaphoid pole to escape from beneath the capitate. row carpectomies. It is hypothesized that the resection
Under load, this displacing scaphoid produces stretch of this synovitic attachment point is responsible for the
and insult to the synovium. In its mildest form, acute relatively low rates of progression to arthritis despite
wrist trauma produces scapholunate (SL) synovitis and continued abnormal scaphoid migration under load.
ligamentous strain without a SL ligament tear. A more A second group with a similar surgical procedure has
substantial ligament tear may result in a displacing been described with 86% of their patients having good to
scaphoid accompanied by chronic synovitis. These wrists excellent results. [18]
are painful and will not tolerate loading. Conservative
treatment consists of splinting and other types of activity In conclusion, inflamed synovium influences adjacent
modification. [16] collagen. This fundamental relationship is the basis for
Surgical management of DWS after 6 months of many of the pathologic conditions of the hand, from
conservative care involves exploration of the SL joint capsular and ligament collagen to bone collagen (the
with excision of the soft tissue synovial mass and any “collasyn theory”). Viewing pathology of the hand in this
associated ganglia. Bony ridging and osteophytes form on manner may enhance our understanding and consequent
the dorsum of the scaphoid and occasionally the lunate treatment of hand conditions. The synovial cells produce a
and are present in every case to some extent [Figure 3]. multitude of molecules and mediators involved in normal
The dorsal ridging is believed to be the synovial joint function as well as inflammatory mediators such as
attachment point responsible for molecular remodeling of cytokines in response to osteoarthritis. [19,20] Lubricin and
collagen and bone due to the synovial inflammation. No hyaluronic acid are two important lubricant molecules
change in scaphoid stability is accomplished. One hundred produced by synovium. Recent evidence has shown
and fifty‑one cases of surgically treated DWS were that these molecules are important in articular cartilage
evaluated and <10% of these wrists required subsequent maintenance and loss of these substances can lead to
scaphoid stabilization (scaphoid‑trapezium‑trapezoid (STT) osteoarthritic degeneration. [21‑23] A reactive synovium
fusion). Wollstein et al. presented results on 80 patients produces factors related to inflammation through
[17]
surgically treated for DWS, with 25% requiring some form participation in multiple pathways. [24‑27] Synovium includes
of further surgery, including 9 STT fusions and 2 proximal mesenchymal stem cells capable of differentiating into
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 2 || Mar 13, 2015 49