Page 26 - Read Online
P. 26
given the elective nature of treatment to improve
patient cosmesis, we believe that the patient report,
while inherently biased, is still an acceptable method of
outcome assessment.
In conclusion, the pilot study did not establish a dose
equivalency between incobotulinumtoxin A (xeomin)
vs. abobotulinumtoxin A (dysport) in the treatment
of dynamic glabellar frown lines in 32 consecutive
patients who previously reported treatment success
with abobotulinumtoxin A for at least 1 year at 4‑month
intervals. By combining the analysis of both the
patient‑reported results and the objective evaluation of
dynamic glabellar muscle activity at 10‑12 weeks following
one treatment session with incoBTX‑A, we found that using
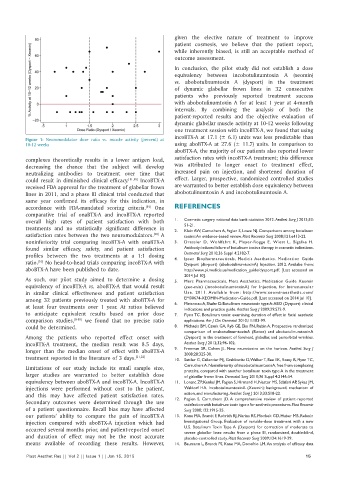
incoBTX‑A at 17.1 (± 6.1) units was less predictable than
Figure 1: Neuromodulator dose ratio vs. muscle activity (percent) at
10‑12 weeks using aboBTX‑A at 27.6 (± 11.7) units. In comparison to
aboBTX‑A, the majority of our patients also reported lower
complexes theoretically results in a lower antigen load, satisfaction rates with incoBTX‑A treatment; this difference
decreasing the chance that the subject will develop was attributed to longer onset to treatment effect,
neutralizing antibodies to treatment over time that increased pain on injection, and shortened duration of
could result in diminished clinical efficacy. [11,18] IncoBTX‑A effect. Larger, prospective, randomized controlled studies
received FDA approval for the treatment of glabellar frown are warranted to better establish dose equivalency between
lines in 2011, and a phase III clinical trial conducted that abobotulinumtoxin A and incobotulinumtoxin A.
same year confirmed its efficacy for this indication, in
accordance with FDA‑mandated scoring criteria. One REFERENCES
[19]
comparative trial of onaBTX‑A and incoBTX‑A reported
overall high rates of patient satisfaction with both 1. Cosmetic surgery national data bank: statistics 2012. Aesthet Surg J 2013;33:
treatments and no statistically significant difference in 2. S1‑21.
Klein AW, Carruthers A, Fagien S, Lowe NJ. Comparisons among botulinum
satisfaction rates between the two neuromodulators. A toxins: An evidence‑based review. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008;121:e413‑22.
[20]
noninferiority trial comparing incoBTX‑A with onaBTX‑A 3. Dressler D, Wohlfahrt K, Meyer‑Rogge E, Wiest L, Bigalke H.
found similar efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction Antibody‑induced failure of botulinum toxin a therapy in cosmetic indications.
profiles between the two treatments at a 1:1 dosing 4. Dermatol Surg 2010;36 Suppl 4:2182‑7.
Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Medicis Aesthetics. Medication Guide
ratio. No head‑to‑head trials comparing incoBTX‑A with Dysport (dis‑port) (abobotulinumtoxinA) Injection. 2012. Availabe from:
[10]
aboBTX‑A have been published to date. http://www.pi.medicis.us/medication_guide/dysport.pdf. [Last accessed on
2014 Jul 10].
As such, our pilot study aimed to determine a dosing 5. Merz Pharmaceuticals, Merz Aesthetics. Medication Guide Xeomin
equivalency of incoBTX‑A vs. aboBTX‑A that would result (zeo‑min) (incobotulinumtoxinA) for Injection, for Intramuscular
in similar clinical effectiveness and patient satisfaction Use. 2011. Available from: http://www.xeominaesthetic.com/
among 32 patients previously treated with aboBTX‑A for EM00674‑XEOMIN‑Medication‑Guide.pdf. [Last accessed on 2014 Jul 10].
at least four treatments over 1 year. At ratios believed 6. Matarasso A, Shafer D. Botulinum neurotoxin type A‑ABO (Dysport): clinical
indications and practice guide. Aesthet Surg J 2009;29:S72‑9.
to anticipate equivalent results based on prior dose 7. Flynn TC. Botulinum toxin: examining duration of effect in facial aesthetic
comparison studies, [8‑10] we found that no precise ratio applications. Am J Clin Dermatol 2010;11:183‑99.
could be determined. 8. Michaels BM, Csank GA, Ryb GE, Eko FN, Rubin A. Prospective randomized
comparison of onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) and abobotulinumtoxinA
Among the patients who reported effect onset with (Dysport) in the treatment of forehead, glabellar, and periorbital wrinkles.
incoBTX‑A treatment, the median result was 8.5 days, Aesthet Surg J 2012;32:96‑102.
longer than the median onset of effect with aboBTX‑A 9. Freeman SR, Cohen JL. New neurotoxins on the horizon. Aesthet Surg J
2008;28:325‑30.
treatment reported in the literature of 3 days. [21,22] 10. Sattler G, Callander MJ, Grablowitz D, Walker T, Bee EK, Rzany B, Flynn TC,
Limitations of our study include its small sample size, Carruthers A. Noninferiority of incobotulinumtoxinA, free from complexing
proteins, compared with another botulinum toxin type A in the treatment
larger studies are warranted to better establish dose of glabellar frown lines. Dermatol Surg 2010;36 Suppl 4:2146‑54.
equivalency between aboBTX‑A and incoBTX‑A. IncoBTX‑A 11. Lorenc ZP, Kenkel JM, Fagien S, Hirmand H, Nestor MS, Sclafani AP, Sykes JM,
injections were performed without cost to the patient, Waldorf HA. IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin): background, mechanism of
and this may have affected patient satisfaction rates. action, and manufacturing. Aesthet Surg J 2013;33:S18‑22.
Secondary outcomes were determined through the use 12. Fagien S, Carruthers JD. A comprehensive review of patient‑reported
satisfaction with botulinum toxin type a for aesthetic procedures. Plast Reconstr
of a patient questionnaire. Recall bias may have affected Surg 2008;122:1915‑25.
our patients’ ability to compare the pain of incoBTX‑A 13. Kane MA, Brandt F, Rohrich RJ, Narins RS, Monheit GD, Huber MB, Reloxin
injection compared with aboBTX‑A injection which had Investigational Group. Evaluation of variable‑dose treatment with a new
occurred several months prior, and patient‑reported onset U.S. Botulinum Toxin Type A (Dysport) for correction of moderate to
severe glabellar lines: results from a phase III, randomized, double‑blind,
and duration of effect may not be the most accurate placebo‑controlled study. Plast Reconstr Surg 2009;124:1619‑29.
means available of recording these results. However, 14. Baumann L, Brandt FS, Kane MA, Donofrio LM. An analysis of efficacy data
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 1 || Jan 15, 2015 15