Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
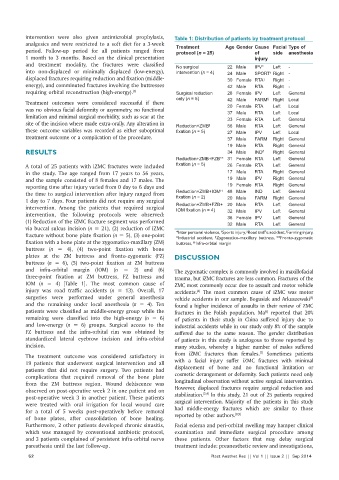
intervention were also given antimicrobial prophylaxis, Table 1: Distribution of patients by treatment protocol
analgesics and were restricted to a soft diet for a 3‑week Treatment Age Gender Cause Facial Type of
period. Follow‑up period for all patients ranged from protocol (n = 25) of side anesthesia
1 month to 3 months. Based on the clinical presentation injury
and treatment modality, the fractures were classified No surgical 22 Male IPV* Left -
into non‑displaced or minimally displaced (low‑energy), intervention (n = 4) 24 Male SPORT Right -
†
displaced fractures requiring reduction and fixation (middle‑ 30 Female RTA ‡ Right -
energy), and comminuted fractures involving the buttresses 42 Male RTA Right -
requiring orbital reconstruction (high‑energy). [3] Surgical reduction 28 Female IPV Left General
only (n = 5) 42 Male FARM § Right Local
Treatment outcomes were considered successful if there 20 Female RTA Left Local
was no obvious facial deformity or asymmetry, no functional 37 Male RTA Left Local
limitation and minimal surgical morbidity, such as scar at the 33 Female RTA Left General
site of the incision where made extra‑orally. Any alteration in Reduction+ZMB 56 Male RTA Left General
||
these outcome variables was recorded as either suboptimal fixation (n = 5) 27 Male IPV Left Local
treatment outcome or a complication of the procedure. 37 Male FARM Right General
19 Male RTA Right General
RESULTS 34 Male IND # Right General
Reduction+ZMB+FZB** 31 Female RTA Left General
A total of 25 patients with iZMC fractures were included fixation (n = 5) 26 Female RTA Left General
in the study. The age ranged from 17 years to 56 years, 17 Male RTA Right General
and the sample consisted of 8 females and 17 males. The 19 Male IPV Right General
reporting time after injury varied from 0 day to 6 days and 19 Female RTA Right General
††
the time to surgical intervention after injury ranged from Reduction+ZMB+IOM 48 Male IND Left General
fixation (n = 2)
1 day to 7 days. Four patients did not require any surgical 20 Male FARM Right General
intervention. Among the patients that required surgical Reduction+ZMB+FZB+ 20 Male RTA Left General
IOM fixation (n = 4)
intervention, the following protocols were observed: 32 Male IPV Left General
Left
General
36 Female IPV
(1) Reduction of the iZMC fracture segment was performed 32 Male RTA Left General
via buccal sulcus incision (n = 21), (2) reduction of iZMC † ‡ §
fracture without bone plate fixation (n = 5), (3) one‑point *Inter personal violence, Sports injury, Road traffic accident, Farming injury,
Industrial accident, Zygomatico‑maxillary buttress, **Fronto‑zygomatic
#
||
fixation with a bone plate at the zygomatico‑maxillary (ZM) buttress, Infra‑orbtial margin
††
buttress (n = 4), (4) two‑point fixation with bone
plates at the ZM buttress and fronto‑zygomatic (FZ) DISCUSSION
buttress (n = 6), (5) two‑point fixation at ZM buttress
and infra‑orbital margin (IOM) (n = 2) and (6) The zygomatic complex is commonly involved in maxillofacial
three‑point fixation at ZM buttress, FZ buttress and trauma, but iZMC fractures are less common. Fractures of the
IOM (n = 4) [Table 1]. The most common cause of ZMC most commonly occur due to assault and motor vehicle
injury was road traffic accidents (n = 13). Overall, 17 accidents. The most common cause of iZMC was motor
[4]
surgeries were performed under general anesthesia vehicle accidents in our sample. Bogusiak and Arkuszewski
[5]
and the remaining under local anesthesia (n = 4). Ten found a higher incidence of assaults in their review of ZMC
patients were classified as middle‑energy group while the fractures in the Polish population. Ma reported that 20%
[6]
remaining were classified into the high‑energy (n = 6) of patients in their study in China suffered injury due to
and low‑energy (n = 6) groups. Surgical access to the industrial accidents while in our study only 8% of the sample
FZ buttress and the infra‑orbital rim was obtained by suffered due to the same reason. The gender distribution
standardized lateral eyebrow incision and infra‑orbital of patients in this study is analogous to those reported by
incision. many studies, whereby a higher number of males suffered
from iZMC fractures than females. Sometimes patients
[7]
The treatment outcome was considered satisfactory in
19 patients that underwent surgical intervention and all with a facial injury suffer iZMC fractures with minimal
patients that did not require surgery. Two patients had displacement of bone and no functional limitation or
complications that required removal of the bone plate cosmetic derangement or deformity. Such patients need only
from the ZM buttress region. Wound dehiscence was longitudinal observation without active surgical intervention.
observed on post‑operative week 2 in one patient and on However, displaced fractures require surgical reduction and
[3,4]
post‑operative week 3 in another patient. These patients stabilization. In this study, 21 out of 25 patients required
were treated with oral irrigation for local wound care surgical intervention. Majority of the patients in this study
had middle‑energy fractures which are similar to those
for a total of 5 weeks post‑operatively before removal reported by other authors. [8,9]
of bone plates, after consolidation of bone healing.
Furthermore, 2 other patients developed chronic sinusitis, Facial edema and peri‑orbital swelling may hamper clinical
which was managed by conventional antibiotic protocol, examination and immediate surgical procedure among
and 3 patients complained of persistent infra‑orbital nerve these patients. Other factors that may delay surgical
paresthesia until the last follow‑up. treatment include: preanesthetic review and investigations,
52 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 2 || Sep 2014