Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
of levels I and II in 277 oral tongue cancer patients. Lydiatt et al.
[35]
concluded that the inclusion of the lower jugular chain with the
supraomohyoid neck dissection had increased the effectiveness of
regional control by 20% to 24%.
Shah et al. found a 3.5% incidence of nodal metastases at levels IV
[68]
and V and a 1.5% incidence of isolated level involvement, outside
the supraomohyoid triangle (level I, II, or III) in their review of the
patterns of cervical metastases in 192 squamous cell carcinoma
of the oral cavity. These findings emphasize the effectiveness of
selective supraomohyoid neck dissection when used electively
to control cervical micrometastases [Figures 2 and 3].
Many pretreatment imaging techniques to diminish the
incidence of occult metastases haven been studied, and
comparative studies have shown USgFNAC to be the most
accurate. However, the sensitivity is only in the range of
50-65% and whether imaging should change the current
management of the cN0 neck remains controversial. In early
OSCC, sentinel node biopsy (SNB) has a sensitivity of 93% for
the detection of occult lymph node metastases. This figure
[62]
is probably even higher in the more experienced centers.
Thus, SNB has a much higher sensitivity and can be used
to better select candidates for neck dissection. Although
the long-term follow-up results of the large European SENT
study are not yet reported, several centers have already
adopted sentinel node biopsy as an alternative to END. In the
American National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN)
guidelines as well as the guidelines of the Dutch Head and
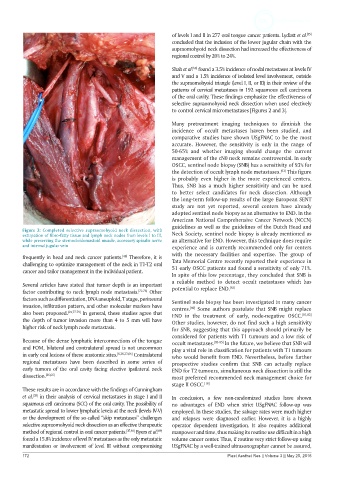
Figure 3: Completed selective supraomohyoid neck dissection, with
extirpation of fibro-fatty tissue and lymph neck nodes from levels I to III, Neck Society, sentinel node biopsy is already mentioned as
while preserving the sternocleidomastoid muscle, accessory spinalis nerve an alternative for END. However, this technique does require
and internal jugular vein experience and is currently recommended only for centers
with the necessary facilities and expertise. The group of
frequently in head and neck cancer patients. Therefore, it is
[48]
challenging to optimize management of the neck in T1-T2 oral Tata Memorial Centre recently reported their experience in
51 early OSCC patients and found a sensitivity of only 71%.
cancer and tailor management in the individual patient.
In spite of this low percentage, they concluded that SNB is
a reliable method to detect occult metastases which has
Several articles have stated that tumor depth is an important potential to replace END. [63]
factor contributing to neck lymph node metastasis. [72-76] Other
factors such as differentiation, DNA aneuploid, T stage, perineural Sentinel node biopsy has been investigated in many cancer
invasion, infiltration pattern, and other molecular markers have centres. Some authors postulate that SNB might replace
[80]
also been proposed. [35,77-79] In general, these studies agree that END in the treatment of early, node-negative OSCC. [81,82]
the depth of tumor invasion more than 4 to 5 mm will have Other studies, however, do not find such a high sensitivity
higher risk of neck lymph node metastasis. for SNB, suggesting that this approach should primarily be
considered for patients with T1 tumours and a low risk of
Because of the dense lymphatic interconnections of the tongue occult metastases. [83-85] In the future, we believe that SNB will
and FOM, bilateral and contralateral spread is not uncommon play a vital role in classification for patients with T1 tumours
in early oral lesions of these anatomic sites. [6,26,33,66] Contralateral who would benefit from END. Nevertheless, before further
regional metastases have been described in some series of prospective studies confirm that SNB can actually replace
early tumors of the oral cavity facing elective ipsilateral neck END for T2 tumours, simultaneous neck dissection is still the
dissection. [26,66] most preferred recommended neck management choice for
stage II OSCC. [16]
These results are in accordance with the findings of Cunningham
et al. in their analysis of cervical metastases in stage I and II In conclusion, a few non-randomized studies have shown
[39]
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the oral cavity. The possibility of no advantages of END when strict USgFNAC follow-up was
metastatic spread to lower lymphatic levels at the neck (levels IV-V) employed. In these studies, the salvage rates were much higher
or the development of the so-called “skip metastases” challenges and relapses were diagnosed earlier. However, it is a highly
selective supraomohyoid neck dissection as an effective therapeutic operator dependent investigation. It also requires additional
method of regional control in oral cancer patients. [35,69] Byers et al. manpower and time, thus making its routine use difficult in a high
[69]
found a 15.8% incidence of level IV metastases as the only metastatic volume cancer center. Thus, if routine very strict follow-up using
manifestation or involvement of level III without compromising USgFNAC by a well-trained ultrasonographer cannot be assured,
172 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016