Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
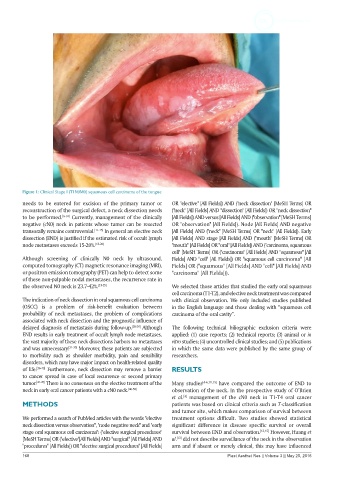
Figure 1: Clinical Stage I (T1N0M0) squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue
needs to be entered for excision of the primary tumor or OR "elective" [All Fields]) AND ("neck dissection" [MeSH Terms] OR
reconstruction of the surgical defect, a neck dissection needs ("neck" [All Fields] AND "dissection" [All Fields]) OR "neck dissection"
to be performed. [6-10] Currently, management of the clinically [All Fields]) AND versus [All Fields] AND ("observation" [MeSH Terms]
negative (cN0) neck in patients whose tumor can be resected OR "observation" [All Fields]). Node [All Fields] AND negative
transorally remains controversial. [11-15] In general an elective neck [All Fields] AND ("neck" [MeSH Terms] OR "neck" [All Fields]). Early
dissection (END) is justified if the estimated risk of occult lymph [All Fields] AND stage [All Fields] AND ("mouth" [MeSH Terms] OR
node metastases exceeds 15-20%. [16-20] "mouth" [All Fields] OR "oral" [All Fields]) AND ("carcinoma, squamous
cell" [MeSH Terms] OR ("carcinoma" [All Fields] AND "squamous" [All
Although screening of clinically N0 neck by ultrasound, Fields] AND "cell" [All Fields]) OR "squamous cell carcinoma" [All
computed tomography (CT) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Fields] OR ("squamous" [All Fields] AND "cell" [All Fields] AND
or positron emission tomography (PET) can help to detect some "carcinoma" [All Fields])).
of these non-palpable nodal metastases, the recurrence rate in
the observed N0 neck is 23.7-42%. [21-25] We selected those articles that studied the early oral squamous
cell carcinoma (T1-T2), and elective neck treatment was compared
The indication of neck dissection in oral squamous cell carcinoma with clinical observation. We only included studies published
(OSCC) is a problem of risk-benefit evaluation between in the English language and those dealing with “squamous cell
probability of neck metastases, the problem of complications carcinoma of the oral cavity”.
associated with neck dissection and the prognostic influence of
delayed diagnosis of metastasis during follow-up. [26-30] Although The following technical biliographic exclusion criteria were
END results in early treatment of occult lymph node metastases, applied: (1) case reports; (2) technical reports; (3) animal or in
the vast majority of these neck dissections harbors no metastases vitro studies; (4) uncontrolled clinical studies; and (5) publications
and was unnecessary. [31-35] Moreover, these patients are subjected in which the same data were published by the same group of
to morbidity such as shoulder morbidity, pain and sensibility researchers.
disorders, which may have major impact on health-related quality
of life. [36-40] Furthermore, neck dissection may remove a barrier RESULTS
to cancer spread in case of local recurrence or second primary
tumor. [41-45] There is no consensus on the elective treatment of the Many studies [4-6,10,15] have compared the outcome of END to
neck in early oral cancer patients with a cN0 neck. [46-50] observation of the neck. In the prospective study of O’Brien
et al. management of the cN0 neck in T1-T4 oral cancer
[4]
METHODS patients was based on clinical criteria such as T-classification
and tumor site, which makes comparison of survival between
We performed a search of PubMed articles with the words "elective treatment options difficult. Two studies showed statistical
neck dissection versus observation", "node negative neck" and "early significant difference in disease specific survival or overall
stage oral squamous cell carcinoma": ("elective surgical procedures" survival between END and observation. [13,15] However, Huang et
[13]
[MeSH Terms] OR ("elective"[All Fields] AND "surgical" [All Fields] AND al. did not describe surveillance of the neck in the observation
"procedures" [All Fields]) OR "elective surgical procedures" [All Fields] arm and if absent or merely clinical, this may have influenced
168 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016