Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
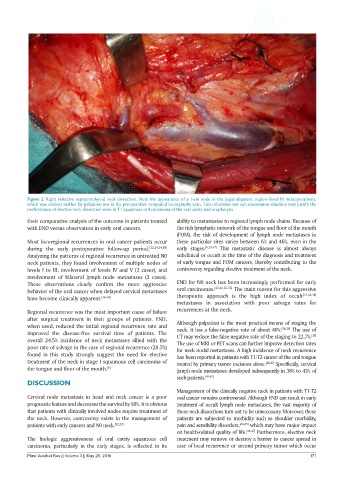
Figure 2: Right selective supraomohyoid neck dissection. Note the appearance of a 1-cm node in the jugulodigastric region (level II) intraoperatively,
which was evident neither by palpation nor in the preoperative computed tomography scan. This otherwise not son uncommon situation may justify the
performance of elective neck dissection even in T1 squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx
their comparative analysis of the outcome in patients treated ability to metastasize to regional lymph node chains. Because of
with END versus observation in early oral cancers. the rich lymphatic network of the tongue and floor of the mouth
(FOM), the risk of development of lymph node metastases in
Most locoregional recurrences in oral cancer patients occur these particular sites varies between 6% and 46%, even in the
during the early postoperative follow-up period. [23,24,34,38] early stages. [6,29-33] This metastatic disease is almost always
Analyzing the patterns of regional recurrence in untreated N0 subclinical or occult at the time of the diagnosis and treatment
neck patients, they found involvement of multiple nodes of of early tongue and FOM cancers, thereby contributing to the
levels I to III, involvement of levels IV and V (2 cases), and controversy regarding elective treatment of the neck.
involvement of bilateral lymph node metastases (2 cases).
These observations clearly confirm the more aggressive END for N0 neck has been increasingly performed for early
behavior of the oral cancer when delayed cervical metastases oral carcinomas. [23,26,33-35] The main reason for this aggressive
have become clinically apparent. [26-30] therapeutic approach is the high index of occult [33,34,36]
metastases in association with poor salvage rates for
Regional recurrence was the most important cause of failure recurrences at the neck.
after surgical treatment in their groups of patients. END, Although palpation is the most practical means of staging the
when used, reduced the initial regional recurrence rate and neck, it has a false-negative rate of about 40%. [38,39] The use of
improved the disease-free survival time of patients. The CT may reduce the false negative rate of the staging to 22.7%.
[38]
overall 24.5% incidence of neck metastases allied with the The use of MRI or PET scans can further improve detection rates
poor rate of salvage in the case of regional recurrence (28.5%) for neck nodal metastases. A high incidence of neck recurrence
found in this study strongly suggest the need for elective has been reported in patients with T1-T2 cancer of the oral tongue
treatment of the neck in stage I squamous cell carcinoma of treated by primary tumor excisions alone. [40,41] Specifically, cervical
the tongue and floor of the mouth. [6] lymph node metastases developed subsequently in 38% to 43% of
such patients. [41-43]
DISCUSSION
Management of the clinically negative neck in patients with T1-T2
Cervical node metastasis in head and neck cancer is a poor oral cancer remains controversial. Although END can result in early
prognostic feature and decreases the survival by 50%. It is obvious treatment of occult lymph node metastases, the vast majority of
that patients with clinically involved nodes require treatment of these neck dissections turn out to be unnecessary. Moreover, these
the neck. However, controversy exists in the management of patients are subjected to morbidity such as shoulder morbidity,
patients with early cancers and N0 neck. [22,23] pain and sensibility disorders, [44,45] which may have major impact
on health-related quality of life. [46,47] Furthermore, elective neck
The biologic aggressiveness of oral cavity squamous cell treatment may remove or destroy a barrier to cancer spread in
carcinoma, particularly in the early stages, is reflected in its case of local recurrence or second primary tumor which occur
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016 171