Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Page 12 of 14 Nakamoto et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2024;11:54 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2024.82
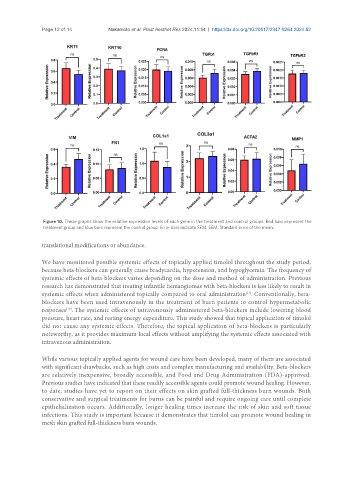
Figure 10. These graphs show the relative expression levels of each gene in the treatment and control groups. Red bars represent the
treatment group and blue bars represent the control group. Error bars indicate SEM. SEM: Standard error of the mean.
translational modifications or abundance.
We have monitored possible systemic effects of topically applied timolol throughout the study period,
because beta-blockers can generally cause bradycardia, hypotension, and hypoglycemia. The frequency of
systemic effects of beta-blockers varies depending on the dose and method of administration. Previous
research has demonstrated that treating infantile hemangiomas with beta-blockers is less likely to result in
systemic effects when administered topically compared to oral administration . Conventionally, beta-
[17]
blockers have been used intravenously in the treatment of burn patients to control hypermetabolic
responses . The systemic effects of intravenously administered beta-blockers include lowering blood
[18]
pressure, heart rate, and resting energy expenditure. This study showed that topical application of timolol
did not cause any systemic effects. Therefore, the topical application of beta-blockers is particularly
noteworthy, as it provides maximum local effects without amplifying the systemic effects associated with
intravenous administration.
While various topically applied agents for wound care have been developed, many of them are associated
with significant drawbacks, such as high costs and complex manufacturing and availability. Beta-blockers
are relatively inexpensive, broadly accessible, and Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved.
Previous studies have indicated that these readily accessible agents could promote wound healing. However,
to date, studies have yet to report on their effects on skin grafted full-thickness burn wounds. Both
conservative and surgical treatments for burns can be painful and require ongoing care until complete
epithelialization occurs. Additionally, longer healing times increase the risk of skin and soft tissue
infections. This study is important because it demonstrates that timolol can promote wound healing in
mesh skin grafted full-thickness burn wounds.