Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Chen et al. Contralateral cerebral ischemia after MMD bypass
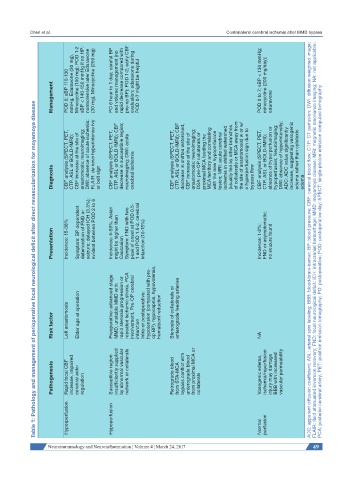
Management POD 0; sBP 110-130 mmHg, Edaravone (30 mg), Minocycline (100 mg); POD 1-2 sBP < 140-150 mmHg if no HP; normotensive later Edaravone (30 mg), Minocycline (200 mg) PO 6 hour to 1 day; careful BP and volume management (no rapid decrease compared with pre-op BP); POD 1-2; early CBF evaluation; edaravone during POD 0-7 might be helpful POD 0 to 7; sBP < 130 mmHg; minocycline (200 mg/day); edaravone
Table 1: Pathology and management of perioperative focal neurological deficit after direct revascularization for moyamoya disease
CBF analysis (SPECT, PET, CTP, ASL or BOLD-fMRI); CBF increase at the site of anastomosis; neuroimaging; DWI: absence of acute ischemia; FLAIR: de novo hyperintense ivy CBF analysis (SPECT, PET, CTP, ASL or BOLD-fMRI); CBF decrease in susceptible region; neuroimaging; DWI: acute CBF analysis (SPECT, PET, CTP, ASL or BOLD-fMRI); CBF decrease in shifted watershed, CBF increase at the site of anastomosis; neuroimaging; DSA: pre-OP col
Diagnosis or belt sign cerebral ischemia bypass flow edema
Presentation Incidence: 15-38% Symptom: BP dependent deterioration of FND or seizure; delayed ICH (3.3%); evident between POD 2 to 6 Incidence: 4-59%, Asian might be higher than Caucasian Symptom: FND with two peak of onset at POD 0.5- 1 and POD 1.5-2, cerebral infarction (10-15%) Incidence: 1-2%; FND or asymptomatic; no seizure found ADC: apparent diffusion coefficient; ASL: arterial spin labeling; BBB: blood-brain-barrier; BP: blood pre
Risk factor Left anastomosis Elder age at operation Preoperative: advanced stage MMD, unstable MMD with rapid stenosis progression or repeated ischemic stroke, PCA involvement, Pre-OP cerebral infarction Intra-or postoperative: hypotension (compared with pre- op BP), hypocapnia, hypovolemia, hematocrit reduction Stenosis of collaterals or anterograde feeding arteries NA
Pathogenesis Rapid focal CBF increase, impaired cerebral auto- regulation Susceptible region insufficiently supplied by abnormal vascular network or collaterals Retrograde blood from STA-MCA bypass conflict with anterograde blood from proximal MCA or collaterals Vasogenic edema, ischemia/reperfusion injury may damage BBB with increased vascular permeability
Hyperperfusion Hypoperfusion Normal perfusion
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ March 24, 2017 49