Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
enzymes, thyroid function, erythrocyte sedimentation mitral valves vegetation.
rate, anti-streptolysin O test, rheumatoid factor, high-
sensitivity C-reactive protein, blood cultures, and DISCUSSION
autoantibody series (such as antinuclear antibodies,
ds-DNA and so on). The test results of pathogens Clinical manifestations of IE have a variety of
(bacteria, viruses and treponema pallidum) were also symptoms and signs. These include fever, arterial
negative in blood. Routine electroencephalogram embolic phenomena (cerebral embolism, renal
showed there was no spike or slow waves. Another embolism, pulmonary embolism, etc.), heart murmur,
test on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) showed no obvious clubbing of fingers and toes, and other symptoms.
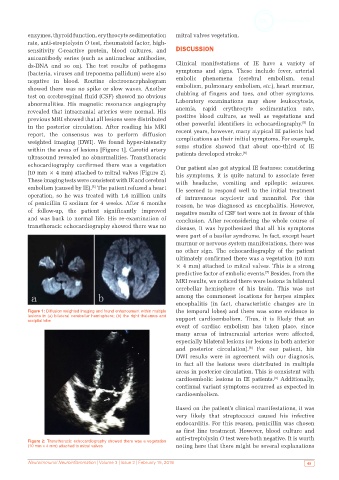
abnormalities. His magnetic resonance angiography Laboratory examinations may show leukocytosis,
revealed that intracranial arteries were normal. His anemia, rapid erythrocyte sedimentation rate,
previous MRI showed that all lesions were distributed positive blood culture, as well as vegetations and
[5]
in the posterior circulation. After reading his MRI other powerful identifiers in echocardiography. In
report, the consensus was to perform diffusion recent years, however, many atypical IE patients had
weighted imaging (DWI). We found hyper-intensity complications as their initial symptoms. For example,
within the areas of lesions [Figure 1]. Carotid artery some studies showed that about one-third of IE
[6]
ultrasound revealed no abnormalities. Transthoracic patients developed stroke.
echocardiography confirmed there was a vegetation Our patient also got atypical IE features: considering
(10 mm × 4 mm) attached to mitral valves [Figure 2]. his symptoms, it is quite natural to associate fever
These imaging tests were consistent with IE and cerebral with headache, vomiting and epileptic seizures.
embolism (caused by IE). The patient refused a heart He seemed to respond well to the initial treatment
[5]
operation, so he was treated with 1.6 million units of intravenous acyclovir and mannitol. For this
of penicillin G sodium for 4 weeks. After 6 months reason, he was diagnosed as encephalitis. However,
of follow-up, the patient significantly improved negative results of CSF test were not in favour of this
and was back to normal life. His re-examination of conclusion. After reconsidering the whole course of
transthoracic echocardiography showed there was no disease, it was hypothesized that all his symptoms
were part of a basilar syndrome. In fact, except heart
murmur or nervous system manifestations, there was
no other sign. The echocardiography of the patient
ultimately confirmed there was a vegetation (10 mm
× 4 mm) attached to mitral valves. This is a strong
predictive factor of embolic events. Besides, from the
[7]
MRI results, we noticed there were lesions in bilateral
cerebellar hemisphere of his brain. This was not
among the commonest locations for herpes simplex
encephalitis (in fact, characteristic changes are in
Figure 1: Diffusion weighted imaging and found enhancement within multiple the temporal lobes) and there was some evidence to
lesions in (a) bilateral cerebellar hemisphere; (b) the right thalamus and support cardioembolism. Thus, it is likely that an
occipital lobe
event of cardiac embolism has taken place, since
many areas of intracranial arteries were affected,
especially bilateral lesions (or lesions in both anterior
[8]
and posterior circulation). For our patient, his
DWI results were in agreement with our diagnosis,
in fact all the lesions were distributed in multiple
areas in posterior circulation. This is consistent with
cardioembolic lesions in IE patients. Additionally,
[9]
continual variant symptoms occurred as expected in
cardioembolism.
Based on the patient’s clinical manifestations, it was
very likely that streptococci caused his infective
endocarditis. For this reason, penicillin was chosen
as first line treatment. However, blood culture and
anti-streptolysin O test were both negative. It is worth
Figure 2: Transthoracic echocardiography showed there was a vegetation
(10 mm × 4 mm) attached to mitral valves noting here that there might be several explanations
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | Issue 2 | February 15, 2016 49