Page 115 - Read Online
P. 115
Anticoagulation for CVT was precluded since he had
bilateral subdural effusions and CVT was secondary
to SIH. After 24 h of bed rest and adequate hydration,
since the patient was very much symptomatic, a
cervical autologous epidural blood patch with 10 mL
of blood was performed under CT guidance and
achieved the resolution of the symptoms within a
week without worsening the CVT. Brain CT taken on
day 5 following epidural blood patch showed mild
reduction in the extent of subdural effusions [Figure
3B]. In addition, the patient showed no residual
symptoms or recurrence at six-month follow-up.
DISCUSSION
Literature clearly defines clinical signs, typical
MRI findings and treatment options of SIH. In an
[3]
intact cranium, the total intracranial volume must be
[4]
constant according to the Monroe-Kellie hypothesis.
SIH usually occurs due to spontaneous CSF leaks
in the inferior cervical and superior thoracic spine.
Mechanical stress, meningeal diverticula and
connective tissue diseases have been reported as the
potential risk factors for the development of SIH.
The Monroe-Kellie hypothesis states that the decrease
in intracranial blood volume is compensated by the
[4]
dilatation of the cerebral veins. Furthermore, CSF
Figure 2: T2 sagittal sequence from the spine MRI showing elliptical high signal
extra axial collection posterior to the spinal cordat T3 to T8 level (as marked by loss reduces the CSF absorption into the cerebral
the arrow, suggestive of CSF leak)
venous sinuses leading to an increase in blood
viscosity in the cerebral compartment.
In our patient, epidural blood patch was performed
earlier within 24 h of conservative therapy since the
patient was very much symptomatic and SIH was
complicated with subdural effusions and CVT.
In 2015, Kapoor and Ahmed did a comprehensive
electronic literature search to include studies that
reported on performance of cervical EBPs in patients
[16]
with CSF leak at the cervical level. Their review
provides Class II level of evidence that cervical EBPs
are safe and effective in reliving positional headache
due to CSF leak. A total of 15 studies, reporting on 19
patients were included. All patients presented with
a headache that increased in the standing position,
and improved in the supine position. All patients
were identified to have a CSF leak at the cervical
level. Eight patients first underwent a lumbar EBP,
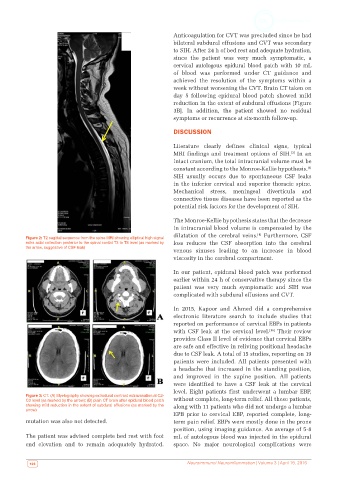
Figure 3: CT. (A) Myelography showing extradural contrast extravasation at C2-
C3 level (as marked by the arrow); (B) plain CT brain after epidural blood patch without complete, long-term relief. All these patients,
showing mild reduction in the extent of subdural effusions (as marked by the along with 11 patients who did not undergo a lumbar
arrow)
EPB prior to cervical EBP, reported complete, long-
mutation was also not detected. term pain relief. EBPs were mostly done in the prone
position, using imaging guidance. An average of 5-8
The patient was advised complete bed rest with foot mL of autologous blood was injected in the epidural
end elevation and to remain adequately hydrated. space. No major neurological complications were
106 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | April 19, 2016