Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
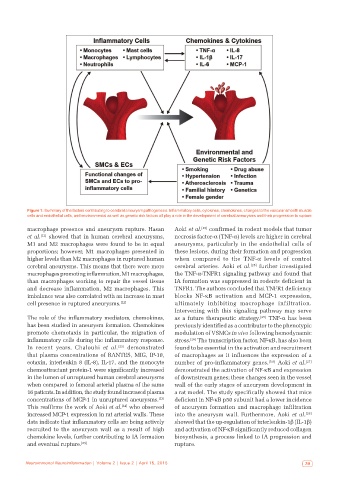
Figure 1: Summary of the factors contributing to cerebral aneurysm pathogenesis. Inflammatory cells, cytokines, chemokines, changes to the vascular smooth muscle
cells and endothelial cells, and environmental as well as genetic risk factors all play a role in the development of cerebral aneurysms and their progression to rupture
macrophage presence and aneurysm rupture. Hasan Aoki et al. [25] confirmed in rodent models that tumor
et al. [22] showed that in human cerebral aneurysms, necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels are higher in cerebral
M1 and M2 macrophages were found to be in equal aneurysms, particularly in the endothelial cells of
proportions; however, M1 macrophages presented in these lesions, during their formation and progression
higher levels than M2 macrophages in ruptured human when compared to the TNF-α levels of control
cerebral aneurysms. This means that there were more cerebral arteries. Aoki et al. [25] further investigated
macrophages promoting inflammation, M1 macrophages, the TNF-α-TNFR1 signaling pathway and found that
than macrophages working to repair the vessel tissue IA formation was suppressed in rodents deficient in
and decrease inflammation, M2 macrophages. This TNFR1. The authors concluded that TNFR1 deficiency
imbalance was also correlated with an increase in mast blocks NF-κB activation and MCP-1 expression,
cell presence in ruptured aneurysms. [22] ultimately inhibiting macrophage infiltration.
Intervening with this signaling pathway may serve
The role of the inflammatory mediators, chemokines, as a future therapeutic strategy. [25] TNF-α has been
has been studied in aneurysm formation. Chemokines previously identified as a contributor to the phenotypic
promote chemotaxis in particular, the migration of modulation of VSMCs in vivo following hemodynamic
inflammatory cells during the inflammatory response. stress. [26] The transcription factor, NF-κB, has also been
In recent years, Chalouhi et al. [23] demonstrated found to be essential in the activation and recruitment
that plasma concentrations of RANTES, MIG, IP-10, of macrophages as it influences the expression of a
eotaxin, interleukin 8 (IL-8), IL-17, and the monocyte number of pro-inflammatory genes. [5,6] Aoki et al. [27]
chemoattractant protein-1 were significantly increased demonstrated the activation of NF-κB and expression
in the lumen of unruptured human cerebral aneurysms of downstream genes; these changes seen in the vessel
when compared to femoral arterial plasma of the same wall of the early stages of aneurysm development in
16 patients. In addition, the study found increased plasma a rat model. The study specifically showed that mice
[23]
concentrations of MCP-1 in unruptured aneurysms. deficient in NF-κB p50 subunit had a lower incidence
[24]
This reaffirms the work of Aoki et al. who observed of aneurysm formation and macrophage infiltration
increased MCP-1 expression in rat arterial walls. These into the aneurysm wall. Furthermore, Aoki et al. [28]
data indicate that inflammatory cells are being actively showed that the up-regulation of interleukin-1β (IL-1β)
recruited to the aneurysm wall as a result of high and activation of NF-κB significantly reduced collagen
chemokine levels, further contributing to IA formation biosynthesis, a process linked to IA progression and
and eventual rupture. [23] rupture.
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 2 | April 15, 2015 79