Page 143 - Read Online
P. 143
2 +
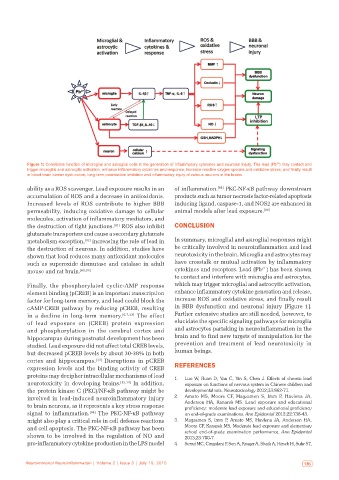
Figure 1: Correlative function of microglial and astroglial cells in the generation of inflammatory cytokines and neuronal injury. The lead (Pb ) may contact and
trigger microglial and astrocytic activation, enhance inflammatory cytokines and response, increase reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress, and finally result
in blood‑brain barrier dysfunction, long‑term potentiation inhibition and inflammatory injury of various neurons in the brains
ability as a ROS scavenger. Lead exposure results in an of inflammation. [85] PKC-NF-κB pathway downstream
accumulation of ROS and a decrease in antioxidants. products such as tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis
Increased levels of ROS contribute to higher BBB inducing ligand, caspase-1, and NOS2 are enhanced in
permeability, inducing oxidative damage to cellular animal models after lead exposure. [86]
molecules, activation of inflammatory mediators, and
the destruction of tight junctions. [81] ROS also inhibit CONCLUSION
glutamate transporters and cause a secondary glutamate
metabolism exception, [82] increasing the role of lead in In summary, microglial and astroglial responses might
the destruction of neurons. In addition, studies have be critically involved in neuroinflammation and lead
shown that lead reduces many antioxidant molecules neurotoxicity in the brain. Microglia and astrocytes may
such as superoxide dismutase and catalase in adult have crosstalk or mutual activation by inflammatory
2 +
mouse and rat brain. [68,83] cytokines and receptors. Lead (Pb ) has been shown
to contact and interfere with microglia and astrocytes,
Finally, the phosphorylated cyclic-AMP response which may trigger microglial and astrocytic activation,
element binding (pCREB) is an important transcription enhance inflammatory cytokine generation and release,
factor for long-term memory, and lead could block the increase ROS and oxidative stress, and finally result
cAMP-CREB pathway by reducing pCREB, resulting in BBB dysfunction and neuronal injury [Figure 1].
in a decline in long-term memory. [6,7,13] The effect Further extensive studies are still needed, however, to
of lead exposure on (CREB) protein expression elucidate the specific signaling pathways for microglia
and phosphorylation in the cerebral cortex and and astrocytes partaking in neuroinflammation in the
hippocampus during postnatal development has been brain and to find new targets of manipulation for the
studied. Lead exposure did not affect total CREB levels, prevention and treatment of lead neurotoxicity in
but decreased pCREB levels by about 30-38% in both human beings.
cortex and hippocampus. [13] Disruptions in pCREB
expression levels and the binding activity of CREB REFERENCES
proteins may decipher intracellular mechanisms of lead 1. Luo W, Ruan D, Yan C, Yin S, Chen J. Effects of chronic lead
neurotoxicity in developing brains. [12,13] In addition, exposure on functions of nervous system in Chinese children and
the protein kinase C (PKC)/NF-κB pathway might be developmental rats. Neurotoxicology 2012;33:862‑71.
involved in lead-induced neuroinflammatory injury 2. Amato MS, Moore CF, Magzamen S, Imm P, Havlena JA,
to brain neurons, as it represents a key stress response Anderson HA, Kanarek MS. Lead exposure and educational
proficiency: moderate lead exposure and educational proficiency
signal to inflammation. [84] The PKC-NF-κB pathway on end‑of‑grade examinations. Ann Epidemiol 2012;22:738‑43.
might also play a critical role in cell defense reactions 3. Magzamen S, Imm P, Amato MS, Havlena JA, Anderson HA,
and cell apoptosis. The PKC-NF-κB pathway has been Moore CF, Kanarek MS. Moderate lead exposure and elementary
school end‑of‑grade examination performance. Ann Epidemiol
shown to be involved in the regulation of NO and 2013;23:700‑7.
pro-inflammatory cytokine production in the LPS model 4. Senut MC, Cingolani P, Sen A, Kruger A, Shaik A, Hirsch H, Suhr ST,
134 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 135