Page 202 - Read Online
P. 202
Tang. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.60 Page 5 of 13
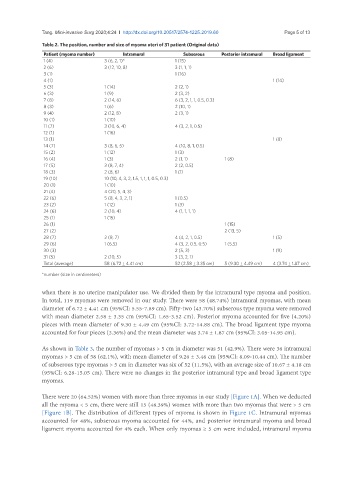
Table 2. The position, number and size of myoma uteri of 31 patient (Original data)
Patient (myoma number) Intramural Subserous Posterior intramural Broad ligament
1 (4) 3 (6, 2, 1)* 1 (15)
2 (6) 3 (12, 10, 8) 3 (1, 1, 1)
3 (1) 1 (16)
4 (1) 1 (14)
5 (3) 1 (14) 2 (2, 1)
6 (3) 1 (9) 2 (3, 2)
7 (8) 2 (14, 6) 6 (3, 2, 1, 1, 0.5, 0.3)
8 (3) 1 (6) 2 (10, 1)
9 (4) 2 (12, 8) 2 (3, 1)
10 (1) 1 (10)
11 (7) 3 (10, 6, 4) 4 (3, 2, 1, 0.5)
12 (1) 1 (16)
13 (1) 1 (8)
14 (7) 3 (8, 6, 5) 4 (10, 8, 1, 0.5)
15 (2) 1 (12) 1 (3)
16 (4) 1 (3) 2 (1, 1) 1 (8)
17 (5) 3 (8, 7, 4) 2 (2, 0.5)
18 (3) 2 (8, 6) 1 (1)
19 (10) 10 (10, 4, 3, 2, 1.5, 1, 1, 1, 0.5, 0.3)
20 (1) 1 (10)
21 (4) 4 (20, 5, 4, 3)
22 (6) 5 (8, 4, 3, 2, 1) 1 (0.5)
23 (2) 1 (12) 1 (3)
24 (6) 2 (10, 4) 4 (1, 1, 1, 1)
25 (1) 1 (15)
26 (1) 1 (15)
27 (2) 2 (13, 5)
28 (7) 2 (8, 7) 4 (4, 2, 1, 0.5) 1 (5)
29 (6) 1 (6.5) 4 (3, 2, 0.5, 0.5) 1 (5.5)
30 (3) 2 (5, 3) 1 (9)
31 (5) 2 (10, 5) 3 (3, 2, 1)
Total (average) 58 (6.72 ± 4.41 cm) 52 (2.58 ± 3.35 cm) 5 (9.30 ± 4.49 cm) 4 (3.74 ± 1.87 cm)
*number (size in centimeters)
when there is no uterine manipulator use. We divided them by the intramural type myoma and position.
In total, 119 myomas were removed in our study. There were 58 (48.74%) intramural myomas, with mean
diameter of 6.72 ± 4.41 cm (95%CI: 5.55-7.89 cm). Fifty-two (43.70%) subserous type myoma were removed
with mean diameter 2.58 ± 3.35 cm (95%CI: 1.65-3.52 cm). Posterior myoma accounted for five (4.20%)
pieces with mean diameter of 9.30 ± 4.49 cm (95%CI: 3.72-14.88 cm). The broad ligament type myoma
accounted for four pieces (3.36%) and the mean diameter was 3.74 ± 1.87 cm (95%CI: 3.05-14.95 cm).
As shown in Table 3, the number of myomas > 5 cm in diameter was 51 (42.9%). There were 36 intramural
myomas > 5 cm of 58 (62.1%), with mean diameter of 9.26 ± 3.46 cm (95%CI: 8.09-10.44 cm). The number
of subserous type myomas > 5 cm in diameter was six of 52 (11.5%), with an average size of 10.67 ± 4.18 cm
(95%CI: 6.28-15.05 cm). There were no changes in the posterior intramural type and broad ligament type
myomas.
There were 20 (64.52%) women with more than three myomas in our study [Figure 1A]. When we deducted
all the myoma < 5 cm, there were still 15 (48.39%) women with more than two myomas that were > 5 cm
[Figure 1B]. The distribution of different types of myoma is shown in Figure 1C. Intramural myomas
accounted for 48%, subserous myoma accounted for 44%, and posterior intramural myoma and broad
ligament myoma accounted for 4% each. When only myomas ≥ 5 cm were included, intramural myoma