Page 170 - Read Online
P. 170
Crema et al. Minimally invasive esophagectomy in achalasia
A B C
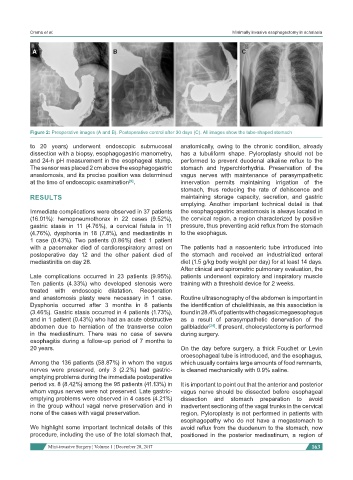
Figure 2: Preoperative images (A and B). Postoperative control after 30 days (C). All images show the tube-shaped stomach
to 20 years) underwent endoscopic submucosal anatomically, owing to the chronic condition, already
dissection with a biopsy, esophagogastric manometry, has a tubuliform shape. Pyloroplasty should not be
and 24-h pH measurement in the esophageal stump. performed to prevent duodenal alkaline reflux to the
The sensor was placed 2 cm above the esophagogastric stomach and hyperchlorhydria. Preservation of the
anastomosis, and its precise position was determined vagus nerves with maintenance of parasympathetic
at the time of endoscopic examination . innervation permits maintaining irrigation of the
[9]
stomach, thus reducing the rate of dehiscence and
RESULTS maintaining storage capacity, secretion, and gastric
emptying. Another important technical detail is that
Immediate complications were observed in 37 patients the esophagogastric anastomosis is always located in
(16.01%): hemopneumothorax in 22 cases (9.52%), the cervical region, a region characterized by positive
gastric stasis in 11 (4.76%), a cervical fistula in 11 pressure, thus preventing acid reflux from the stomach
(4.76%), dysphonia in 18 (7.8%), and mediastinitis in to the esophagus.
1 case (0.43%). Two patients (0.86%) died: 1 patient
with a pacemaker died of cardiorespiratory arrest on The patients had a nasoenteric tube introduced into
postoperative day 12 and the other patient died of the stomach and received an industrialized enteral
mediastinitis on day 28. diet (1.5 g/kg body weight per day) for at least 14 days.
After clinical and spirometric pulmonary evaluation, the
Late complications occurred in 23 patients (9.95%). patients underwent expiratory and inspiratory muscle
Ten patients (4.33%) who developed stenosis were training with a threshold device for 2 weeks.
treated with endoscopic dilatation. Reoperation
and anastomosis plasty were necessary in 1 case. Routine ultrasonography of the abdomen is important in
Dysphonia occurred after 3 months in 8 patients the identification of cholelithiasis, as this association is
(3.46%). Gastric stasis occurred in 4 patients (1.73%), found in 28.4% of patients with chagasic megaesophagus
and in 1 patient (0.43%) who had an acute obstructive as a result of parasympathetic denervation of the
abdomen due to herniation of the transverse colon gallbladder [24] . If present, cholecystectomy is performed
in the mediastinum. There was no case of severe during surgery.
esophagitis during a follow-up period of 7 months to
20 years. On the day before surgery, a thick Fouchet or Levin
oroesophageal tube is introduced, and the esophagus,
Among the 136 patients (58.87%) in whom the vagus which usually contains large amounts of food remnants,
nerves were preserved, only 3 (2.2%) had gastric- is cleaned mechanically with 0.9% saline.
emptying problems during the immediate postoperative
period vs. 8 (8.42%) among the 95 patients (41.13%) in It is important to point out that the anterior and posterior
whom vagus nerves were not preserved. Late gastric- vagus nerve should be dissected before esophageal
emptying problems were observed in 4 cases (4.21%) dissection and stomach preparation to avoid
in the group without vagal nerve preservation and in inadvertent sectioning of the vagal trunks in the cervical
none of the cases with vagal preservation. region. Pyloroplasty is not performed in patients with
esophagopathy who do not have a megastomach to
We highlight some important technical details of this avoid reflux from the duodenum to the stomach, now
procedure, including the use of the total stomach that, positioned in the posterior mediastinum, a region of
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 163