Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Page 6 of 15 Kumar et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2018;2:19 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.26
Bladder
Division of superior vesical artery
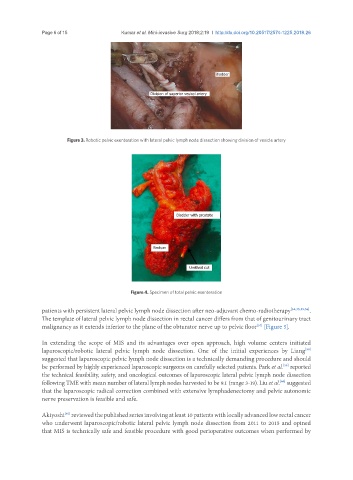
Figure 3. Robotic pelvic exenteration with lateral pelvic lymph node dissection showing division of vesicle artery
Bladder with prostate
Rectum
Urethral cut
Figure 4. Specimen of total pelvic exenteration
patients with persistent lateral pelvic lymph node dissection after neo-adjuvant chemo-radiotherapy [34,35,55,56] .
The template of lateral pelvic lymph node dissection in rectal cancer differs from that of genitourinary tract
malignancy as it extends inferior to the plane of the obturator nerve up to pelvic floor [Figure 5].
[57]
In extending the scope of MIS and its advantages over open approach, high volume centers initiated
laparoscopic/robotic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection. One of the initial experiences by Liang
[58]
suggested that laparoscopic pelvic lymph node dissection is a technically demanding procedure and should
be performed by highly experienced laparoscopic surgeons on carefully selected patients. Park et al. reported
[59]
the technical feasibility, safety, and oncological outcomes of laparoscopic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection
following TME with mean number of lateral lymph nodes harvested to be 9.1 (range 3-19). Liu et al. suggested
[60]
that the laparoscopic radical correction combined with extensive lymphadenectomy and pelvic autonomic
nerve preservation is feasible and safe.
Akiyoshi reviewed the published series involving at least 10 patients with locally advanced low rectal cancer
[61]
who underwent laparoscopic/robotic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection from 2011 to 2015 and opined
that MIS is technically safe and feasible procedure with good perioperative outcomes when performed by