Page 65 - Read Online
P. 65
Page 8 of 13 Tang et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2024;8:24 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.04
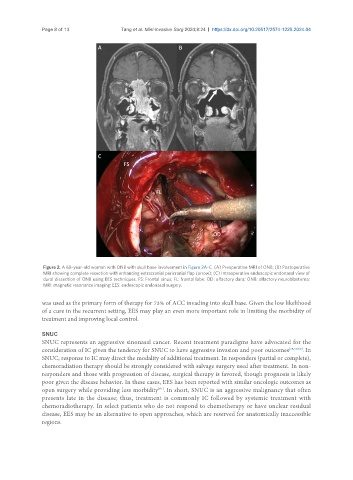
Figure 2. A 68-year-old woman with ONB with skull base involvement in Figure 2A-C. (A) Preoperative MRI of ONB; (B) Postoperative
MRI showing complete resection with enhancing extracranial pericranial flap (arrow); (C) Intraoperative endoscopic endonasal view of
dural dissection of ONB using EES techniques. FS: Frontal sinus; FL: frontal lobe; OD: olfactory dura; ONB: olfactory neuroblastoma;
MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; EES: endoscopic endonasal surgery.
was used as the primary form of therapy for 73% of ACC invading into skull base. Given the low likelihood
of a cure in the recurrent setting, EES may play an even more important role in limiting the morbidity of
treatment and improving local control.
SNUC
SNUC represents an aggressive sinonasal cancer. Recent treatment paradigms have advocated for the
consideration of IC given the tendency for SNUC to have aggressive invasion and poor outcomes [38,59,60] . In
SNUC, response to IC may direct the modality of additional treatment. In responders (partial or complete),
chemoradiation therapy should be strongly considered with salvage surgery used after treatment. In non-
responders and those with progression of disease, surgical therapy is favored, though prognosis is likely
poor given the disease behavior. In these cases, EES has been reported with similar oncologic outcomes as
open surgery while providing less morbidity . In short, SNUC is an aggressive malignancy that often
[61]
presents late in the disease; thus, treatment is commonly IC followed by systemic treatment with
chemoradiotherapy. In select patients who do not respond to chemotherapy or have unclear residual
disease, EES may be an alternative to open approaches, which are reserved for anatomically inaccessible
regions.