Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Singh et al. Mini-invasive Surg. 2025;9:28 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.75 Page 5 of 25
Figure 5. Coronal CT image of skull base foramina. SOF: Superior orbital fissure; FR: foramen rotundum; OC: optic canal. Onodi air cells
(yellow arrows), anatomical variant. CT: Computed tomography.
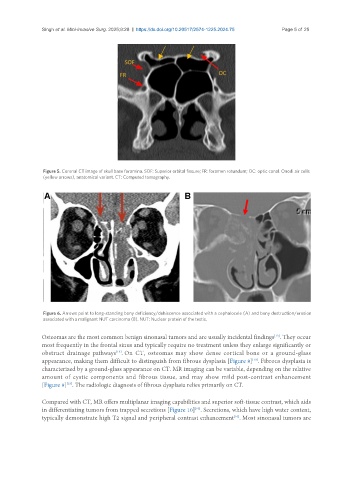
Figure 6. Arrows point to long-standing bony deficiency/dehiscence associated with a cephalocele (A) and bony destruction/erosion
associated with a malignant NUT carcinoma (B). NUT: Nuclear protein of the testis.
[13]
Osteomas are the most common benign sinonasal tumors and are usually incidental findings . They occur
most frequently in the frontal sinus and typically require no treatment unless they enlarge significantly or
[13]
obstruct drainage pathways . On CT, osteomas may show dense cortical bone or a ground-glass
appearance, making them difficult to distinguish from fibrous dysplasia [Figure 8] . Fibrous dysplasia is
[13]
characterized by a ground-glass appearance on CT. MR imaging can be variable, depending on the relative
amount of cystic components and fibrous tissue, and may show mild post-contrast enhancement
[Figure 9] . The radiologic diagnosis of fibrous dysplasia relies primarily on CT.
[13]
Compared with CT, MR offers multiplanar imaging capabilities and superior soft-tissue contrast, which aids
in differentiating tumors from trapped secretions [Figure 10] . Secretions, which have high water content,
[10]
typically demonstrate high T2 signal and peripheral contrast enhancement . Most sinonasal tumors are
[10]