Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Kim et al. Common diseases mimicking lumbar disc herniation
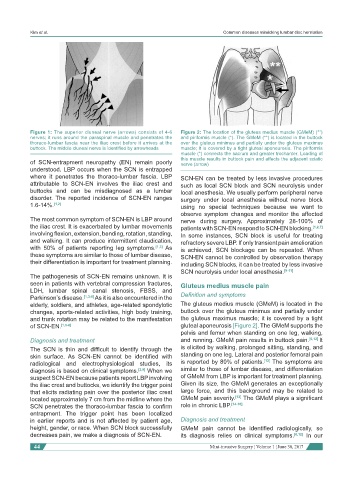
Figure 1: The superior cluneal nerve (arrows) consists of 4-6 Figure 2: The location of the gluteus medius muscle (GMeM) (**)
nerves; it runs around the paraspinal muscle and penetrates the and piriformis muscle (*). The GMeM (**) is located in the buttock
thoraco-lumbar fascia near the iliac crest before it arrives at the over the gluteus minimus and partially under the gluteus maximus
buttock. The middle cluneal nerve is identified by arrowheads muscle; it is covered by a tight gluteal aponeurosis. The piriformis
muscle (*) connects the sacrum and greater trochanter. Loading of
of SCN-entrapment neuropathy (EN) remain poorly this muscle results in buttock pain and affects the adjacent sciatic
nerve (arrow)
understood. LBP occurs when the SCN is entrapped
where it penetrates the thoraco-lumbar fascia. LBP SCN-EN can be treated by less invasive procedures
attributable to SCN-EN involves the iliac crest and such as local SCN block and SCN neurolysis under
buttocks and can be misdiagnosed as a lumbar local anesthesia. We usually perform peripheral nerve
disorder. The reported incidence of SCN-EN ranges surgery under local anesthesia without nerve block
1.6-14%. [1,2] using no special techniques because we want to
observe symptom changes and monitor the affected
The most common symptom of SCN-EN is LBP around nerve during surgery. Approximately 28-100% of
the iliac crest. It is exacerbated by lumbar movements patients with SCN-EN respond to SCN-EN blocking. [1,2,7]
involving flexion, extension, bending, rotation, standing, In some instances, SCN block is useful for treating
and walking. It can produce intermittent claudication, refractory severe LBP. If only transient pain amelioration
with 50% of patients reporting leg symptoms. [1,3] As is achieved, SCN blockage can be repeated. When
these symptoms are similar to those of lumbar disease, SCN-EN cannot be controlled by observation therapy
their differentiation is important for treatment planning. including SCN blocks, it can be treated by less invasive
SCN neurolysis under local anesthesia. [9-11]
The pathogenesis of SCN-EN remains unknown. It is
seen in patients with vertebral compression fractures, Gluteus medius muscle pain
LDH, lumbar spinal canal stenosis, FBSS, and
Parkinson’s disease. [1,3-6] As it is also encountered in the Definition and symptoms
elderly, soldiers, and athletes, age-related spondylotic The gluteus medius muscle (GMeM) is located in the
changes, sports-related activities, high body training, buttock over the gluteus minimus and partially under
and trunk rotation may be related to the manifestation the gluteus maximus muscle; it is covered by a tight
of SCN-EN. [1,5-8] gluteal aponeurosis [Figure 2]. The GMeM supports the
pelvis and femur when standing on one leg, walking,
Diagnosis and treatment and running. GMeM pain results in buttock pain. [6,12] It
The SCN is thin and difficult to identify through the is elicited by walking, prolonged sitting, standing, and
skin surface. As SCN-EN cannot be identified with standing on one leg. Lateral and posterior femoral pain
radiological and electrophysiological studies, its is reported by 80% of patients. [12] The symptoms are
diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms. [2,9] When we similar to those of lumbar disease, and differentiation
suspect SCN-EN because patients report LBP involving of GMeM from LBP is important for treatment planning.
the iliac crest and buttocks, we identify the trigger point Given its size, the GMeM generates an exceptionally
that elicits radiating pain over the posterior iliac crest large force, and this background may be related to
located approximately 7 cm from the midline where the GMeM pain severity. [13] The GMeM plays a significant
SCN penetrates the thoraco-lumbar fascia to confirm role in chronic LBP. [14-16]
entrapment. The trigger point has been localized
in earlier reports and is not affected by patient age, Diagnosis and treatment
height, gender, or race. When SCN block successfully GMeM pain cannot be identified radiologically, so
decreases pain, we make a diagnosis of SCN-EN. its diagnosis relies on clinical symptoms. [6,12] In our
44 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017