Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Ohara et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar laminectomy
A B
C D
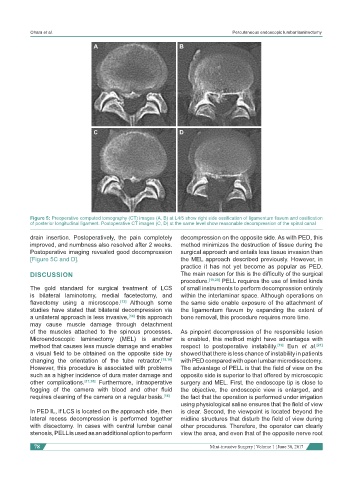
Figure 5: Preoperative computed tomography (CT) images (A, B) at L4/5 show right side ossification of ligamentum flavum and ossification
of posterior longitudinal ligament. Postoperative CT images (C, D) at the same level show reasonable decompression of the spinal canal
drain insertion. Postoperatively, the pain completely decompression on the opposite side. As with PED, this
improved, and numbness also resolved after 2 weeks. method minimizes the destruction of tissue during the
Postoperative imaging revealed good decompression surgical approach and entails less tissue invasion than
[Figure 5C and D]. the MEL approach described previously. However, in
practice it has not yet become as popular as PED.
DISCUSSION The main reason for this is the difficulty of the surgical
procedure. [19,20] PELL requires the use of limited kinds
The gold standard for surgical treatment of LCS of small instruments to perform decompression entirely
is bilateral laminotomy, medial facetectomy, and within the interlaminar space. Although operations on
flavectomy using a microscope. [13] Although some the same side enable exposure of the attachment of
studies have stated that bilateral decompression via the ligamentum flavum by expanding the extent of
a unilateral approach is less invasive, [14] this approach bone removal, this procedure requires more time.
may cause muscle damage through detachment
of the muscles attached to the spinous processes. As pinpoint decompression of the responsible lesion
Microendoscopic laminectomy (MEL) is another is enabled, this method might have advantages with
method that causes less muscle damage and enables respect to postoperative instability. [19] Eun et al. [21]
a visual field to be obtained on the opposite side by showed that there is less chance of instability in patients
changing the orientation of the tube retractor. [15,16] with PED compared with open lumbar microdiscectomy.
However, this procedure is associated with problems The advantage of PELL is that the field of view on the
such as a higher incidence of dura mater damage and opposite side is superior to that offered by microscopic
other complications. [17,18] Furthermore, intraoperative surgery and MEL. First, the endoscope tip is close to
fogging of the camera with blood and other fluid the objective, the endoscopic view is enlarged, and
requires cleaning of the camera on a regular basis. [16] the fact that the operation is performed under irrigation
using physiological saline ensures that the field of view
In PED IL, if LCS is located on the approach side, then is clear. Second, the viewpoint is located beyond the
lateral recess decompression is performed together midline structures that disturb the field of view during
with discectomy. In cases with central lumbar canal other procedures. Therefore, the operator can clearly
stenosis, PELL is used as an additional option to perform view the area, and even that of the opposite nerve root
78 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017