Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Kim et al. Common diseases mimicking lumbar disc herniation
The etiology of TTS has been ascribed to tumors;
changes in anatomical structures due to trauma;
and idiopathic factors such as tortuous vessels,
hypertrophy of the flexor retinaculum, and fibrosis with
a variety of origins. Compression of tortuous arteries
and veins can elicit TTS, although a tortuous vein may
be a normal variation. TTS was idiopathic in 18-69% of
patients. [58-60]
The symptoms are sensory disturbance in the sole of
the affected foot, paresthesia, a foreign-body sensation
like walking on gravel, cold sensation, and burning or
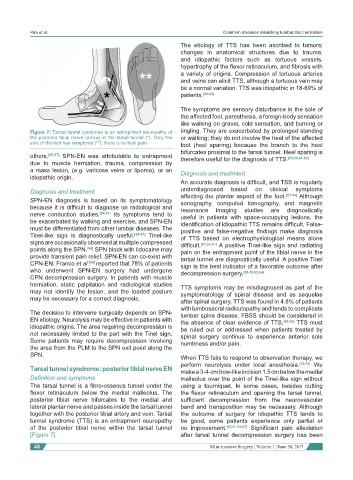
Figure 7: Tarsal tunnel syndrome is an entrapment neuropathy of tingling. They are exacerbated by prolonged standing
the posterior tibial nerve (arrow) in the tarsal tunnel (*). Only the or walking; they do not involve the heel of the affected
sole of the foot has symptoms (**); there is no heel pain foot (heel sparing) because the branch to the heel
bifurcates proximal to the tarsal tunnel. Heel sparing is
others, [55-57] SPN-EN was attributable to entrapment therefore useful for the diagnosis of TTS. [58,59,61-63]
due to muscle herniation, trauma, compression by
a mass lesion, (e.g. varicose veins or lipoma), or an Diagnosis and treatment
idiopathic origin.
An accurate diagnosis is difficult, and TSS is regularly
Diagnosis and treatment underdiagnosed based on clinical [61-64] symptoms
SPN-EN diagnosis is based on its symptomatology affecting the plantar aspect of the foot. Although
sonography, computed tomography, and magnetic
because it is difficult to diagnose on radiological and resonance imaging studies are diagnostically
nerve conduction studies. [54-57] Its symptoms tend to useful in patients with space-occupying lesions, the
be exacerbated by walking and exercise, and SPN-EN identification of idiopathic TTS remains difficult. False-
must be differentiated from other lumbar diseases. The positive and false-negative findings make diagnosis
Tinel-like sign is diagnostically useful. [54-57] Tinel-like of TTS based on electrophysiological means alone
signs are occasionally observed at multiple compressed difficult. [61,65-67] A positive Tinel-like sign and radiating
points along the SPN. [54] SPN block with lidocaine may pain on the entrapment point of the tibial nerve in the
provide transient pain relief. SPN-EN can co-exist with tarsal tunnel are diagnostically useful. A positive Tinel
CPN-EN; Franco et al. [56] reported that 78% of patients sign is the best indicator of a favorable outcome after
who underwent SPN-EN surgery had undergone decompression surgery. [58,59,62,64]
CPN decompression surgery. In patients with muscle
herniation, static palpitation and radiological studies TTS symptoms may be misdiagnosed as part of the
may not identify the lesion, and the loaded posture symptomatology of spinal disease and as sequelae
may be necessary for a correct diagnosis. after spinal surgery. TTS was found in 4.8% of patients
with lumbosacral radiculopathy and tends to complicate
The decision to intervene surgically depends on SPN- lumbar spine disease. FBSS should be considered in
EN etiology. Neurolysis may be effective in patients with the absence of clear evidence of TTS. [68,69] TTS must
idiopathic origins. The area requiring decompression is be ruled out or addressed when patients treated by
not necessarily limited to the part with the Tinel sign. spinal surgery continue to experience anterior sole
Some patients may require decompression involving numbness and/or pain.
the area from the PLM to the SPN exit point along the
SPN. When TTS fails to respond to observation therapy, we
perform neurolysis under local anesthesia. [62,63] We
Tarsal tunnel syndrome: posterior tibial nerve EN make a 3-4-cm bow-like incision 1.5 cm below the medial
Definition and symptoms malleolus over the point of the Tinel-like sign without
The tarsal tunnel is a fibro-osseous tunnel under the using a tourniquet. In some cases, besides cutting
flexor retinaculum below the medial malleolus. The the flexor retinaculum and opening the tarsal tunnel,
posterior tibial nerve bifurcates to the medial and sufficient decompression from the neurovascular
lateral plantar nerve and passes inside the tarsal tunnel band and transposition may be necessary. Although
together with the posterior tibial artery and vein. Tarsal the outcome of surgery for idiopathic TTS tends to
tunnel syndrome (TTS) is an entrapment neuropathy be good, some patients experience only partial or
of the posterior tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel no improvement. [60,61,64,67] Significant pain alleviation
[Figure 7]. after tarsal tunnel decompression surgery has been
48 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017