Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Page 4 of 14 Farinha et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2023;7:38 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2023.50
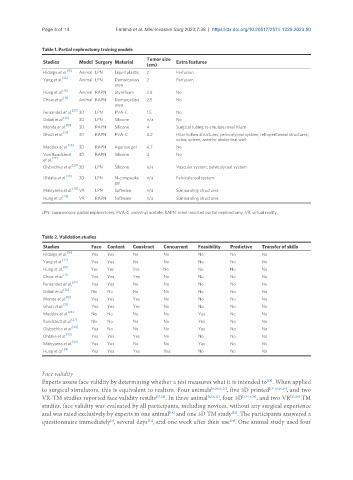
Table 1. Partial nephrectomy training models
Tumor size
Studies Model Surgery Material Extra features
(cm)
[16]
Hidalgo et al. Animal LPN Liquid plastic 2 Perfusion
Yang et al. [32] Animal LPN Demarcation 2 Perfusion
area
Hung et al. [18] Animal RAPN Styrofoam 3.8 No
[11]
Chow et al. Animal RAPN Demarcation 2.5 No
area
Fernandez et al. [20] 3D LPN PVA-C 1.5 No
Golab et al. [25] 3D LPN Silicone n/a No
[19]
Monda et al. 3D RAPN Silicone 4 Surgical tubing to emulate renal hilum
Ghazi et al. [21] 3D RAPN PVA-C 4.2 Hilar hollow structures; pelvicalyceal system; retroperitoneal structures;
colon; spleen; anterior abdominal wall
[26]
Maddox et al. 3D RAPN Agarose gel 4.7 No
Von Rundstedt 3D RAPN Silicone 4 No
et al. [27]
Glybochko et al. [28] 3D LPN Silicone n/a Vascular system; pelvicalyceal system
Ohtake et al. [33] 3D LPN N-composite n/a Pelvicalyceal system
gel
Makiyama et al. [30] VR LPN Software n/a Surrounding structures
[29]
Hung et al. VR RAPN Software n/a Surrounding structures
LPN: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy; PVA-C: polyvinyl acetate; RAPN: robot-assisted partial nephrectomy; VR: virtual reality.
Table 2. Validation studies
Studies Face Content Construct Concurrent Feasibility Predictive Transfer of skills
[16]
Hidalgo et al. Yes Yes No No No No No
[32]
Yang et al. Yes Yes No No No No No
Hung et al. [18] Yes Yes Yes No No No No
[11]
Chow et al. Yes Yes Yes No No No No
Fernandez et al. [20] Yes Yes No No No No No
[25]
Golab et al. No No No No No No No
Monda et al. [19] Yes Yes Yes No No No No
[21]
Ghazi et al. Yes Yes Yes No No No No
Maddox et al. [26] No No No No Yes No No
[27]
Rundstedt et al. No No No No Yes No No
Glybochko et al. [28] Yes No No No Yes No No
[33]
Ohtake et al. Yes Yes Yes No No No No
[30]
Makiyama et al. Yes Yes No No Yes No No
[29]
Hung et al. Yes Yes Yes Yes No No No
Face validity
Experts assess face validity by determining whether a test measures what it is intended to . When applied
[18]
to surgical simulators, this is equivalent to realism. Four animals [9,14,16,31] , five 3D printed [17-19,26,29] , and two
VR-TM studies reported face validity results [27,28] . In three animal [9,16,31] , four 3D [17-19,29] , and two VR [27,28] TM
studies, face validity was evaluated by all participants, including novices, without any surgical experience
[14]
[26]
and was rated exclusively by experts in one animal and one 3D TM study . The participants answered a
questionnaire immediately , several days , and one week after their use . One animal study used four
[9]
[31]
[14]