Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Ghaseminejad et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2022;6:111-25 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.49 Page 121
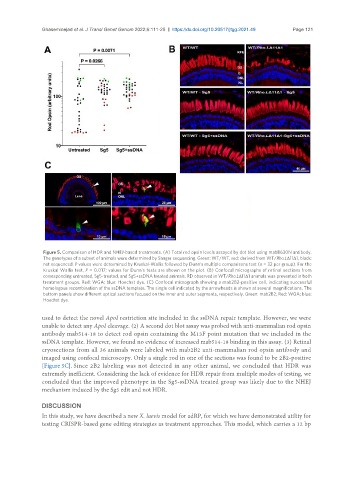
Figure 5. Comparison of HDR and NHEJ-based treatments. (A) Total rod opsin levels assayed by dot blot using mabB630N antibody.
The genotypes of a subset of animals were determined by Sanger sequencing. Green: WT/WT, red: derived from WT/Rho.LΔ11Δ1, black:
not sequenced. P values were determined by Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (n = 32 per group). For the
Kruskal Wallis test, P = 0.017; values for Dunn’s tests are shown on the plot. (B) Confocal micrographs of retinal sections from
corresponding untreated, Sg5-treated, and Sg5+ssDNA treated animals. RD observed in WT/Rho.LΔ11Δ1 animals was prevented in both
treatment groups. Red: WGA; blue: Hoechst dye. (C) Confocal micrograph showing a mab2B2-positive cell, indicating successful
homologous recombination of the ssDNA template. The single cell indicated by the arrowheads is shown at several magnifications. The
bottom panels show different optical sections focused on the inner and outer segments, respectively. Green: mab2B2; Red: WGA; blue:
Hoechst dye.
used to detect the novel ApoI restriction site included in the ssDNA repair template. However, we were
unable to detect any ApoI cleavage. (2) A second dot blot assay was probed with anti-mammalian rod opsin
antibody mab514-18 to detect rod opsin containing the M13F point mutation that we included in the
ssDNA template. However, we found no evidence of increased mab514-18 binding in this assay. (3) Retinal
cryosections from all 36 animals were labeled with mab2B2 anti-mammalian rod opsin antibody and
imaged using confocal microscopy. Only a single rod in one of the sections was found to be 2B2-positive
[Figure 5C]. Since 2B2 labeling was not detected in any other animal, we concluded that HDR was
extremely inefficient. Considering the lack of evidence for HDR repair from multiple modes of testing, we
concluded that the improved phenotype in the Sg5-ssDNA treated group was likely due to the NHEJ
mechanism induced by the Sg5 edit and not HDR.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we have described a new X. laevis model for adRP, for which we have demonstrated utility for
testing CRISPR-based gene editing strategies as treatment approaches. This model, which carries a 12 bp