Page 109 - Read Online
P. 109
Dewsbury et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2024;8:85-101 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.58 Page 95
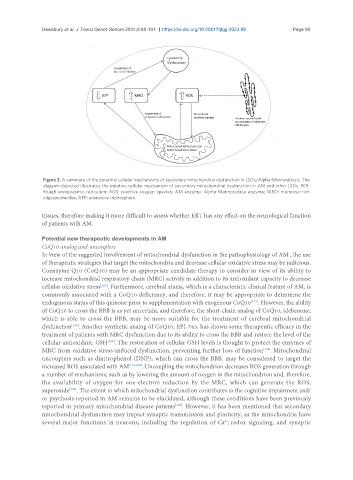
Figure 3. A summary of the potential cellular mechanisms of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction in LSDs/Alpha-Mannosidosis. The
diagram depicted illustrates the putative cellular mechanism of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction in AM and other LSDs. RER:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum; ROS: reactive oxygen species; AM enzyme: Alpha-Mannosidase enzyme; MRO: mannose-rich
oligosaccharides; ATP: adenosine triphosphate.
tissues, therefore making it more difficult to assess whether ERT has any effect on the neurological function
of patients with AM.
Potential new therapeutic developments in AM
CoQ10 analog and uncouplers
In view of the suggested involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of AM , the use
of therapeutic strategies that target the mitochondria and decrease cellular oxidative stress may be judicious.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) may be an appropriate candidate therapy to consider in view of its ability to
increase mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) activity in addition to its antioxidant capacity to decrease
[123]
cellular oxidative stress . Furthermore, cerebral ataxia, which is a characteristic clinical feature of AM, is
commonly associated with a CoQ10 deficiency, and therefore, it may be appropriate to determine the
[123]
endogenous status of this quinone prior to supplementation with exogenous CoQ10 . However, the ability
of CoQ10 to cross the BBB is as yet uncertain, and therefore, the short-chain analog of CoQ10, idebenone,
which is able to cross the BBB, may be more suitable for the treatment of cerebral mitochondrial
[123]
dysfunction . Another synthetic analog of CoQ10, EPI-743, has shown some therapeutic efficacy in the
treatment of patients with MRC dysfunction due to its ability to cross the BBB and restore the level of the
cellular antioxidant, GSH . The restoration of cellular GSH levels is thought to protect the enzymes of
[123]
MRC from oxidative stress-induced dysfunction, preventing further loss of function . Mitochondrial
[123]
uncouplers such as dinitrophenol (DNP), which can cross the BBB, may be considered to target the
increased ROS associated with AM [113,124] . Uncoupling the mitochondrion decreases ROS generation through
a number of mechanisms, such as by lowering the amount of oxygen in the mitochondrion and, therefore,
the availability of oxygen for one-electron reduction by the MRC, which can generate the ROS,
superoxide . The extent to which mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the cognitive impairment and/
[125]
or psychosis reported in AM remains to be elucidated, although these conditions have been previously
reported in primary mitochondrial disease patients . However, it has been mentioned that secondary
[125]
mitochondrial dysfunction may impact synaptic transmission and plasticity, as the mitochondria have
several major functions in neurons, including the regulation of Ca , redox signaling, and synaptic
2+