Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Page 6 of 11 Nguyen et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2018;2:19 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2018.20
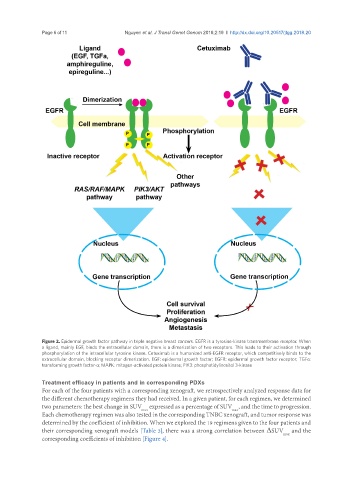
Figure 2. Epidermal growth factor pathway in triple negative breast cancers. EGFR is a tyrosine-kinase transmembrane receptor. When
a ligand, mainly EGF, binds the extracellular domain, there is a dimerization of two receptors. This leads to their activation through
phosphorylation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase. Cetuximab is a humanized anti-EGFR receptor, which competitively binds to the
extracellular domain, blocking receptor dimerization. EGF: epidermal growth factor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; TGFɑ:
transforming growth factor-ɑ; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; PIK3: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Treatment efficacy in patients and in corresponding PDXs
For each of the four patients with a corresponding xenograft, we retrospectively analyzed response data for
the different chemotherapy regimens they had received. In a given patient, for each regimen, we determined
two parameters: the best change in SUV expressed as a percentage of SUV , and the time to progression.
max
max
Each chemotherapy regimen was also tested in the corresponding TNBC xenograft, and tumor response was
determined by the coefficient of inhibition. When we explored the 19 regimens given to the four patients and
their corresponding xenograft models [Table 3], there was a strong correlation between ΔSUV and the
max
corresponding coefficients of inhibition [Figure 4].