Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Kim et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:34-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.14 Page 45
Figure 7. 11 DNS attacks. DNS: Domain Name System; DGA: domain generation algorithm
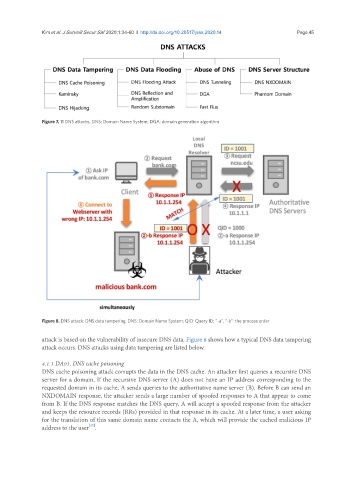
Figure 8. DNS attack: DNS data tampering. DNS: Domain Name System; QID: Query ID; “-a”, “-b”: the process order
attack is based on the vulnerability of insecure DNS data. Figure 8 shows how a typical DNS data tampering
attack occurs. DNS attacks using data tampering are listed below.
4.1.1 DA01. DNS cache poisoning
DNS cache poisoning attack corrupts the data in the DNS cache. An attacker first queries a recursive DNS
server for a domain. If the recursive DNS server (A) does not have an IP address corresponding to the
requested domain in its cache, A sends queries to the authoritative name server (B). Before B can send an
NXDOMAIN response, the attacker sends a large number of spoofed responses to A that appear to come
from B. If the DNS response matches the DNS query, A will accept a spoofed response from the attacker
and keeps the resource records (RRs) provided in that response in its cache. At a later time, a user asking
for the translation of this same domain name contacts the A, which will provide the cached malicious IP
[27]
address to the user .