Page 55 - Read Online
P. 55
Page 48 Kim et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:34-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.14
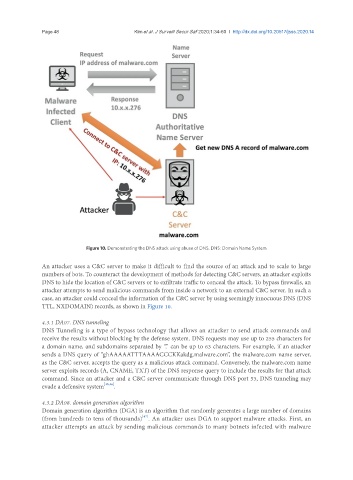
Figure 10. Demonstrating the DNS attack using abuse of DNS. DNS: Domain Name System
An attacker uses a C&C server to make it difficult to find the source of an attack and to scale to large
numbers of bots. To counteract the development of methods for detecting C&C servers, an attacker exploits
DNS to hide the location of C&C servers or to exfiltrate traffic to conceal the attack. To bypass firewalls, an
attacker attempts to send malicious commands from inside a network to an external C&C server. In such a
case, an attacker could conceal the information of the C&C server by using seemingly innocuous DNS (DNS
TTL, NXDOMAIN) records, as shown in Figure 10.
4.3.1 DA07. DNS tunneling
DNS Tunneling is a type of bypass technology that allows an attacker to send attack commands and
receive the results without blocking by the defense system. DNS requests may use up to 255 characters for
a domain name, and subdomains separated by “.” can be up to 63 characters. For example, if an attacker
sends a DNS query of “ghAAAAATTTAAAACCCKKakdg.malware.com”, the malware.com name server,
as the C&C server, accepts the query as a malicious attack command. Conversely, the malware.com name
server exploits records (A, CNAME, TXT) of the DNS response query to include the results for that attack
command. Since an attacker and a C&C server communicate through DNS port 53, DNS tunneling may
evade a defensive system [45,46] .
4.3.2 DA08. domain generation algorithm
Domain generation algorithm (DGA) is an algorithm that randomly generates a large number of domains
[47]
(from hundreds to tens of thousands) . An attacker uses DGA to support malware attacks. First, an
attacker attempts an attack by sending malicious commands to many botnets infected with malware