Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Kim et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:34-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.14 Page 49
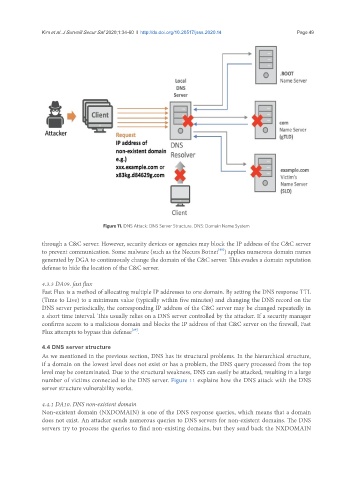
Figure 11. DNS Attack: DNS Server Structure. DNS: Domain Name System
through a C&C server. However, security devices or agencies may block the IP address of the C&C server
[48]
to prevent communication. Some malware (such as the Necurs Botnet ) applies numerous domain names
generated by DGA to continuously change the domain of the C&C server. This evades a domain reputation
defense to hide the location of the C&C server.
4.3.3 DA09. fast flux
Fast Flux is a method of allocating multiple IP addresses to one domain. By setting the DNS response TTL
(Time to Live) to a minimum value (typically within five minutes) and changing the DNS record on the
DNS server periodically, the corresponding IP address of the C&C server may be changed repeatedly in
a short time interval. This usually relies on a DNS server controlled by the attacker. If a security manager
confirms access to a malicious domain and blocks the IP address of that C&C server on the firewall, Fast
[49]
Flux attempts to bypass this defense .
4.4 DNS server structure
As we mentioned in the previous section, DNS has its structural problems. In the hierarchical structure,
if a domain on the lowest level does not exist or has a problem, the DNS query processed from the top
level may be contaminated. Due to the structural weakness, DNS can easily be attacked, resulting in a large
number of victims connected to the DNS server. Figure 11 explains how the DNS attack with the DNS
server structure vulnerability works.
4.4.1 DA10. DNS non-existent domain
Non-existent domain (NXDOMAIN) is one of the DNS response queries, which means that a domain
does not exist. An attacker sends numerous queries to DNS servers for non-existent domains. The DNS
servers try to process the queries to find non-existing domains, but they send back the NXDOMAIN