Page 48 - Read Online
P. 48
Kim et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:34-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.14 Page 41
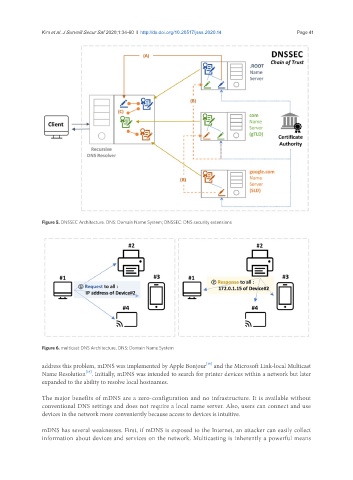
Figure 5. DNSSEC Architecture. DNS: Domain Name System; DNSSEC: DNS security extensions
Figure 6. multicast DNS Architecture. DNS: Domain Name System
[20]
address this problem, mDNS was implemented by Apple Bonjour and the Microsoft Link-local Multicast
[21]
Name Resolution . Initially, mDNS was intended to search for printer devices within a network but later
expanded to the ability to resolve local hostnames.
The major benefits of mDNS are a zero-configuration and no infrastructure. It is available without
conventional DNS settings and does not require a local name server. Also, users can connect and use
devices in the network more conveniently because access to devices is intuitive.
mDNS has several weaknesses. First, if mDNS is exposed to the Internet, an attacker can easily collect
information about devices and services on the network. Multicasting is inherently a powerful means