Page 137 - Read Online
P. 137
Page 6 of 18 Chong et al. J Mater Inf 2023;3:21 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jmi.2023.17
Table 3. Measured chemical compositions of the as-prepared alloys
Alloys Al (at. %) M (at. %) Pt (at. %)
Pt Al 12 11.78 0 Balance
88
Pt Al Cr 11.82 6.21 Balance
82 12 6
Pt Al Hf 6 11.64 6.17 Balance
12
82
Pt Al Ta 11.72 6.06 Balance
82 12 6
M: Cr, Hf, and Ta.
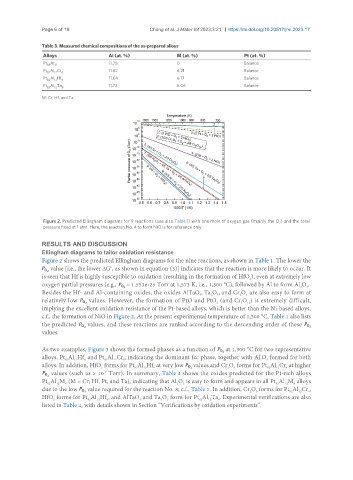
Figure 2. Predicted Ellingham diagrams for 9 reactions (see also Table 1) with one mole of oxygen gas (mainly the O ) and the total
2
pressure fixed at 1 atm. Here, the reaction No. 4 to form NiO is for reference only.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Ellingham diagrams to tailor oxidation resistance
Figure 2 shows the predicted Ellingham diagrams for the nine reactions, as shown in Table 1. The lower the
P value [i.e., the lower ΔG , as shown in equation (3)] indicates that the reaction is more likely to occur. It
o
o2
is seen that Hf is highly susceptible to oxidation (resulting in the formation of HfO ), even at extremely low
2
oxygen partial pressures (e.g., P = 1.553e-25 Torr at 1,573 K, i.e., 1,300 °C), followed by Al to form Al O .
3
2
o2
Besides the Hf- and Al-containing oxides, the oxides AlTaO , Ta O , and Cr O are also easy to form at
4
2
3
5
2
relatively low P values. However, the formation of PtO and PtO (and Cr O ) is extremely difficult,
o2
12
5
2
implying the excellent oxidation resistance of the Pt-based alloys, which is better than the Ni-based alloys,
c.f., the formation of NiO in Figure 2. At the present experimental temperature of 1,300 °C, Table 1 also lists
the predicted P values, and these reactions are ranked according to the descending order of these P
o2
o2
values.
As two examples, Figure 3 shows the formed phases as a function of P at 1,300 °C for two representative
o2
alloys, Pt Al Hf and Pt Al Cr , indicating the dominant fcc phase, together with Al O formed for both
2
6
12
82
82
6
12
3
alloys. In addition, HfO forms for Pt Al Hf at very low P values and Cr O forms for Pt Al Cr at higher
6
o2
3
2
2
82
12
6
12
82
P values (such as > 10 Torr). In summary, Table 4 shows the oxides predicted for the Pt-rich alloys
-7
o2
Pt Al M (M = Cr, Hf, Pt, and Ta), indicating that Al O is easy to form and appears in all Pt Al M alloys
82
6
2
82
6
12
12
3
due to the low P value required for the reaction No. 8; c.f., Table 1. In addition, Cr O forms for Pt Al Cr ,
12
o2
3
6
82
2
HfO forms for Pt Al Hf , and AlTaO and Ta O form for Pt Al Ta . Experimental verifications are also
6
4
12
2
82
12
6
82
2
5
listed in Table 4, with details shown in Section “Verifications by oxidation experiments”.