Page 123 - Read Online
P. 123
Liu et al. J Mater Inf 2023;3:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jmi.2023.19 Page 9 of 17
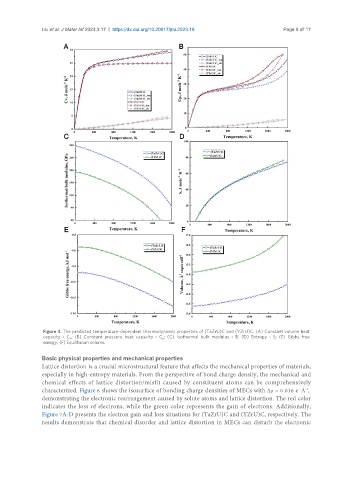
Figure 4. The predicted temperature-dependent thermodynamic properties of (TaZrU)C and (YZrU)C. (A) Constant volume heat
capacity - C ; (B) Constant pressure heat capacity - C ; (C) Isothermal bulk modulus - B; (D) Entropy - S; (E) Gibbs free
V p
energy; (F) Equilibrium volume.
Basic physical properties and mechanical properties
Lattice distortion is a crucial microstructural feature that affects the mechanical properties of materials,
especially in high-entropy materials. From the perspective of bond charge density, the mechanical and
chemical effects of lattice distortion/misfit caused by constituent atoms can be comprehensively
characterized. Figure 6 shows the isosurface of bonding charge densities of MECs with Δρ = 0.016 e Å ,
- -3
demonstrating the electronic rearrangement caused by solute atoms and lattice distortion. The red color
indicates the loss of electrons, while the green color represents the gain of electrons. Additionally,
Figure 7A-D presents the electron gain and loss situations for (TaZrU)C and (YZrU)C, respectively. The
results demonstrate that chemical disorder and lattice distortion in MECs can disturb the electronic